The system redirects users to a new page where they can create a unique user ID and password.
- The transporter does not need an E-way bill when they use a non-motorized mode of transportation.
- The transporter does not need an E-way bill when they transport goods under Customs inspection or by sea.
- The Ministry of Defense moves products due to defense formation as a consignor or consignee, and no E-way bill is require for that.
- The transporter does not need to generate an E-way bill for empty cargo containers.
E-way bills under GST became applicable for inter-state transactions on April 1, 2018, and for all intra-state transactions on June 1, 2018.
What is eWay Bill, and how are you Impacted?
E-way bills are electronic documents that must carried by anyone in charge of a conveyance transporting items worth more than fifty thousand rupees. The registered people or transporters responsible for the movement of goods on consignment can produce the way Bill from the GST Common Portal before the start of such movement.
The system generates a unique E-way bill number (EBN) immediately when the user creates an E-way bill. The source, recipient, and transporter all have access to this EBN.
When is the eway Bill issued?
- You must generate an e-way bill if the value of the consignment to be transported exceeds Rs. 50,000
The system issues a waybill when suppliers supply, return, or receive supplies from unregistered individuals.
- Associated with supply
- Reasons other than supply (for example, a return)
- Inward supply’ from an unregistered individual
The supply could be one of the following:
- A supply made in exchange for money in the process of business
- It may involve a payment that is directly related to business activities or not.
- In certain instances, a supply is provided without any compensation.
As a result, for any type of movement, eWay Bills must be generated on the common portal.
Even if the value of goods is less than Rs. 50,000, a eway bill must generate for specific designated goods.
- The transporter must create an E-way bill when they transport goods across state lines to the job-worker.
- In the instance of inter-state transport of handicraft goods by a GST-exempt dealer
Who can issue an e-way bill?
If both the supply and the receiver are unregistered, the E-way might be given by a registered supply/registered individual, an unregistered individual, or a transporter.
Registered Supplier/ Receiver
Generate an E-way Bill for moving goods worth more than ₹50,000. If the value of the items is less than Rs 50,000, a registered individual or the transporter may choose to create and carry an eWay bill.
Unregistered Persons
When an unregistered person makes a supply to a registered person, an e-Way Bill must be generated; in this case, the receiver must guarantee that all compliance requirements are completed.
Transporter
Transporters who transport products by road, air, rail, etc., must also generate an e-Way Bill if the supplier has not developed one.
In which situation does one not require a waybill?
A lot of situations do not necessitate the use of an e-way Bill.
- The transporter does not need to generate an E-way bill when they carry goods from a port, airport, air cargo complex, or land customs station to an Inland Container Depot (ICD) or Container Freight Station (CFS) for customs clearance.
- There is no need to file Part B of the eway bill when the distance between the consignor/ consignee and the transporter is less than 10 km, and both parties are in the same state.
- The transporter does not need an E-way bill when they use a non-motorized mode of transportation.The transporter does not need an E-way bill when they transport goods under Customs inspection or by sea.
- The Ministry of Defense moves products due to defense formation as a consignor or consignee, and no E-way bill is require.
- The transporter does not need to generate an E-way bill for empty cargo containers.
How can you register on the eWay bill system?
You can access the e-way bill portal, www.ewaybill.nic.in, dedicated to issuing e-way bills. To do so, a user must enroll in the site using his GSTIN number.
Why do you need an E-way bill?
E-way bills are necessary to ship products worth more than Rs. 50,000 and promise to enable speedier movement of commodities through a streamlined portal-driven payment system.
Which type of documentation give to the transporter during goods transit?
The transporter must carry the tax invoice/bill of supply/delivery challan and the E-way bill copy during goods transit.
How many components make up an eWay bill?
The system divides the E-way bill into two parts: Part A and Part B. Part A should include information on the consignor/ consignee and the items, whereas Part B should consist of information about the carrier and the vehicle.
What is the validity of the eWay bill?
When the distance is less than 100 kilometers, the e-way bill is valid for one day. Each additional 100 kilometers or portion thereof increases validity by one day. If the distance is 635 km, the validity period is seven days; if the distance is 356 km, the validity period is four days.
E-Way Bill Registration
The e-way bill is available to three sorts of taxpayers. Registered suppliers, registered or unregistered transporters, and unregistered suppliers are among them. The following steps outline the registration process for taxpayers and registered transporters:
Step 1: Navigate to https://ewaybillgst.gov.in to access the e-way bill gateway.
Step 2: Hover your cursor over ‘Registration’ at the top of the page. A drop-down menu will appear, from which you must choose ‘e-Way Bill Registration.’
Step 3: On the new screen, enter your GST Identification Number, input the captcha code, and click ‘Go’.
Step 4: The system redirects users to a new page where they must generate and validate a One-Time Password (OTP).
Step 5: On this screen, your GSTIN, name, trade name, and address will be auto-populated. After double-checking the information and determining it is correct, click the ‘Send OTP’ button. Users must input the OTP and verify it by clicking the ‘Verify OTP’ button.
Step 6: The system redirects users to a new page where they can create a unique user ID and password.
How to login to E-Waybill System
Taxpayers can connect to the eway portal after registering with a user ID and password.
Step 1: Visit https://www.ewaybillgst.gov.in/Login.aspx to log in.
Step 2: Enter your User ID and Password. If a user forgets his login credentials, he can click on ‘Forgot User ID’/’Forgot TransID’/’Forgot Password’.
Step 3: Enter valid Captcha information and click Log in.
E-Way Bill Validity
The following table details the validity of an e-Way bill:
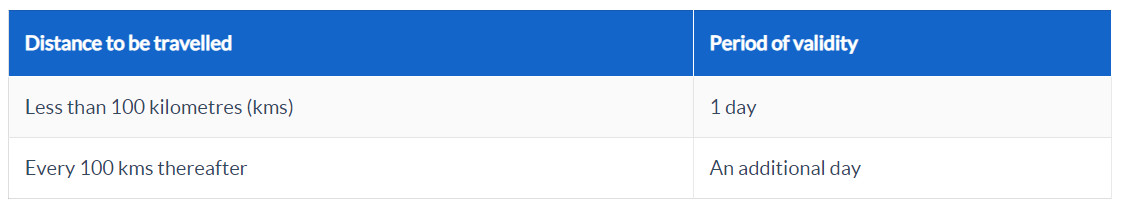
The validity period begins with the generation of the E-Way bill. The commissioner may grant an extension of the validity period for the transfer of certain commodities. The notification will include information on the extension.
The E-Way’s validity for over-dimensional freight is listed in the table below:
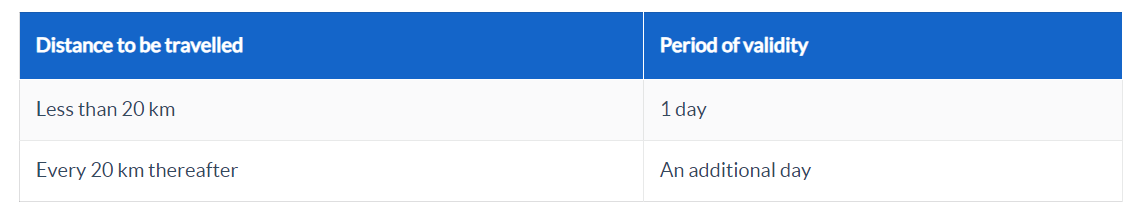
E-Way Bill Exemptions
The following situations do not require an E-way bill:
- A non-motorized vehicle conveys items.
- If customs seals the goods being transported and transports them under customs control.
- In the case of transit freight moving to or from Bhutan or Nepal.
- If the cargo containers being transported are not complete.
- No E-Way bill is required if the consignor is the State Government, the Central Government, or a local government, and the items are carried by rail.
- The transporter must not generate an e-way bill when transferring commodities for customs clearance from airports, ports, land customs stations, or air cargo to a Container Freight Station or an Inland Container Depot.
- If the transporter carries items with a customs seal from another customs station to a customs station or from an Inland Container Depot to a customs port, no e-way bill is required.
Suppose the consignor transfers products from a business location to the location where the goods must be weighed and vice versa. The maximum distance, however, must be 20 kilometers, and the delivery challan must be carried. - If the GST laws for the Union Territory say that the items being carried do not require an E-Way bill.
E-Way Bill Rules
Since the adoption of e-way bills in India in April 2018, the number of goods transactions between states in India has surged dramatically. India’s states and union territories have also expressed interest in generating e-way bills.
People have also received financial rewards if the threshold limit for particular things falls below a certain level. For example, Tamil Nadu excused the generation of e-way bills if the threshold amount fell below Rs.1 lakh.
E-Way Bill Format
Part A and Part B of the e-way Bill are separate documents. Part A contains information on the invoice. Below information must provided:
- The number of the transport paperwork.
- Details on why the transportation is being provided.
- The HSN code must be specified. The HSN code that must be provided will vary depending on the turnover.
- Consignment price.
- The challan number.
- Pin code (specifies the delivery location of the items).
- GSTIN of the beneficiary.
Status of Implementation of eWay Bill in India
Since the adoption of eWay bills in India in April 2018, the volume of goods transactions across states in India has surged dramatically. India’s states and union territories have also expressed interest in issuing eWay invoices. People have also received financial rewards if the threshold limit for particular things falls below a certain level. Tamil Nadu, for example, excused the generation of eWay bills if the threshold amount was less than Rs.1 lakh.
Penalty for Not Generating an E-Way Bill
Failure to generate an E-Way Bill can result in a penalty of ₹10,000. Authorities may detain or seize the vehicle transporting the goods and the goods themselves.
When should I extend the E-Way Bill’s validity?
If the consignment does not arrive at its destination due to one of the following circumstances, the validity of the E-Way Bill can be extended:
- Delay in transshipment
- Accidental transportation
- Issues of law and order during transportation
- Natural disaster
- In case there is any delay due to a breakdown
Wrapping It Up
E-way bills, e-invoicing, and GST are vital in today’s corporate sector because they are mandated by the government. To stay ahead in business, a proper solution that meets all of the criteria of current business scenarios and requirements is essential.
FAQs
-
What is an e-way bill?
Electronic Way Bill (E-Way Bill) is essentially a compliance mechanism in which the person causing the movement of goods uploads the appropriate information prior to the start of the movement of goods and generates an e-way bill on the GST portal via a digital interface.
-
Is the eWay bill required?
Yes, an E-Way Bill is mandatory if the value of goods being transported exceeds ₹50,000
-
Who is responsible for paying the eWay bill?
- The person in charge of the conveyance must carry the E-Way Bill.
-
What is the difference between an invoice and an eWay bill?
While an E-Invoice records transaction and tax information, an E-Way Bill is necessary when the value exceeds Rs. 50,000.
-
What is the km limit for an e-way bill?
400 kilometers
-
What are the drawbacks of the EWAY bill?
The bill extension generates numerous waybill numbers from a single dispatch or invoice.
-
What exactly is URP in an e-way Bill?
Unregistered Person is abbreviated as URP. If one party is unregistered, you must include URP in the e-way bill.
-
What if I don’t get the OTP on my registered cellphone number while producing the e-way bill?
If you do not receive the OTP on my registered mobile number, you can obtain it using your registered email address.
-
What is the distinction between an invoice and an eWay bill?
While an E-Invoice records transactions and tax information, an E-Way Bill is necessary when the value exceeds Rs. 50,000.
-
Can we produce an EWAY charge after the product has been delivered?
Before items can be transported by road, an e-way bill must be issued. That is, the moment the E-Way charge is generated is unrelated to the invoice date. As a result, the E-way bill can be created after the invoice date.
