Introduction
As per the GST regulations established by the Government of India, the Electronic Way Bill, commonly referred to as the E-Way Bill, has become a mandatory requirement for the transportation of goods exceeding the value of Rs.This decision-making process should be based on a thorough understanding of logistics, regulatory requirements, and the goal of ensuring accuracy in E-Way Bill documentation. 50,000.
Any individual involved in the transportation of goods within India, where the value of the goods crosses Rs. 50,000, is required to possess and carry the E-Way Bill. This documentation is electronically generated through the E-Way Bill Portal – www.ewaybillgst.gov.in before transporting goods in a vehicle.
One must remember for certain specified goods, the generation of the e-way bill is obligatory. Even if the consignment’s value is less than Rs. 50,000.
How to generate an E-Way Bill
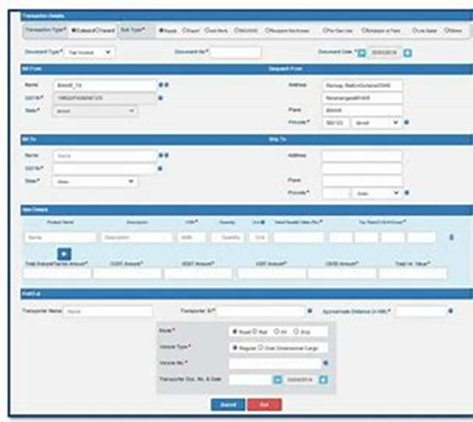
To generate an E-Way Bill, the consigner needs specific information: the invoice, bill of supply, or delivery challan, along with the transporter’s ID (for road transport), vehicle number, transport document number, and the date of the document (for rail, air, or water transport).
Once the e-way bill is generated, a distinctive Eway Bill Number (EBN) is assigned, which is subsequently accessible to the supplier, recipient, and transporter involved in the transportation process. Subsequently, it is essential to share the allocated EBN with the transporter responsible for conveying the goods.
Further, this value of Rs. 50,000 can be for each invoice or the aggregate of all invoices in a vehicle. The responsibility of generating the E-Way Bill lies with the seller or consigner, though the transporter can step in if the seller fails to initiate the process.
Importance of a valid transporter ID
The importance of a valid transporter ID and accurate vehicle details in E-Waybill generation cannot be overstated. These details safeguard against legal complications, ensuring compliance with GST laws and avoiding penalties and fines. Additionally, accuracy in information facilitates smooth transportation, preventing unnecessary delays at checkpoints and tolls, and ultimately ensuring the timely delivery of goods.
Ensuring a valid transporter ID and accurate vehicle details is not merely a procedural formality but a critical component of legal compliance. Moreover, this acts as a deterrent against the misuse of the E-Way Bill system. Allowing only authorized and legitimate transporters to handle the transportation of goods. Moreover, the real-time tracking feature of the E-Way Bill system relies heavily on accurate vehicle information, offering transparency and traceability throughout the transportation process.
Furthermore, non-compliance with GST laws can lead to severe legal repercussions, including hefty penalties and fines. The GST regime places a high premium on accurate documentation, and any oversight in providing the correct transporter ID or vehicle details could expose businesses to legal challenges.
To mitigate this risk, businesses must adopt a meticulous approach to data accuracy and consistently adhere to the guidelines stipulated by the GST authorities.
Advantages of having an E-Way Bill
- Accurate information about the transporter’s ID and vehicle details is fundamental for the seamless movement of goods. When it comes to logistics, any discrepancy or error in these details can lead to delays at various checkpoints. Moreover, smooth passage through check-posts and tolls is contingent on the precision of the information provided in the E-Way Bill.
- Timely and efficient transportation is not only crucial for meeting delivery schedules but also impacts the overall efficiency of the supply chain. By prioritizing the accuracy of transporter ID and vehicle details, businesses can optimize their logistical operations.
- One of the primary objectives of implementing the E-Way Bill system is to prevent the misuse of goods transportation. In this regard, accurate transporter ID and vehicle details serve as a robust safeguard against unauthorized individuals or entities attempting to exploit the system.
- By ensuring that only legitimate and authorized transporters are associated with the movement of goods, businesses can contribute to the overall integrity and reliability of the E-Way Bill process. This preventive measure also adds an additional layer of security to the entire supply chain ecosystem.
Source: SaralGST
- Real-time tracking of goods is a transformative feature facilitated by the E-Way Bill system. Accurate vehicle information also ensures this feature functions effectively. The ability to monitor the movement of goods in real time not only enhances transparency but also provides stakeholders with valuable insights into the status and location of their shipments. This becomes particularly crucial in scenarios where time-sensitive deliveries are involved or when businesses need to respond promptly to any unforeseen challenges in transit. For businesses operating in dynamic environments, tracking functionality becomes a strategic asset.
- Accurate information in the E-Way Bill is not only essential for logistics and legal compliance but also for ensuring the correct application of GST. The E-Way Bill serves as a critical document for tax authorities to verify the legitimacy of the goods in transit. Any discrepancy in the transporter ID or vehicle details can lead to errors in tax calculations, potentially resulting in financial implications for both the business and the government. By prioritizing accuracy in these details, businesses also contribute to the integrity of the taxation system, preventing any inadvertent loss of revenue for the government.
Also Read: Benefits Of E-Way Bill Registration
Source: alertax.in
Practical Issues and Solutions
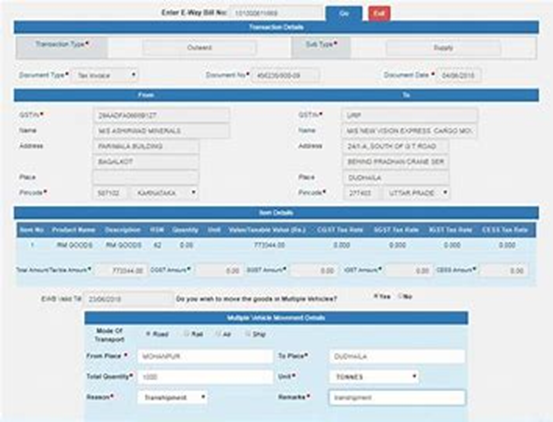
- The scenario of multiple invoices for the same customer supplied through the same truck presents a logistical and administrative challenge. Businesses need to carefully evaluate whether generating multiple E-Way Bills is the most efficient approach or if consolidating them into a single E-Way Bill is a viable option. Moreover. Each decision has implications for the tracking, verification, and compliance processes. Striking the right balance requires a nuanced understanding of the specific business context, the nature of goods being transported, and the regulatory landscape.
- When goods from a single invoice are simultaneously moved in multiple vehicles, businesses face the intricate task of coordinating E-Way Bill generation for this scenario. This situation demands a comprehensive approach to documentation and compliance. Businesses must explore solutions that align with the E-Way Bill framework while ensuring accuracy and coherence in the details provided for each vehicle. Navigating this complexity requires a proactive stance and adopting streamlined processes that accommodate such unique scenarios within the regulatory framework.
Source: Saginfotech
- For unregistered transporters, obtaining a unique 15-digit number known as TRANSIN or Transporter ID is a prerequisite for E-Way Bill compliance. This registration process, while straightforward, demands attention to detail and timely completion. Businesses also engaging with unregistered transporters should proactively guide them through the enrollment process, emphasizing the importance of obtaining and correctly using the assigned TRANSIN in E-Way Bills. This also collaborative approach contributes to a smoother and more efficient goods transportation ecosystem.
- The suspension of GSTIN poses challenges for E-Way Bill generation. However, businesses need to be aware that a suspended GSTIN, whether acting as a recipient or transporter, can still receive a generated E-Way Bill. Navigating the nuances of E-Way Bill compliance during the suspension period requires a clear understanding of the regulations. Businesses must align their processes to account for the temporary restrictions associated with suspended GSTINs, ensuring that they avoid any disruptions in the transportation flow.
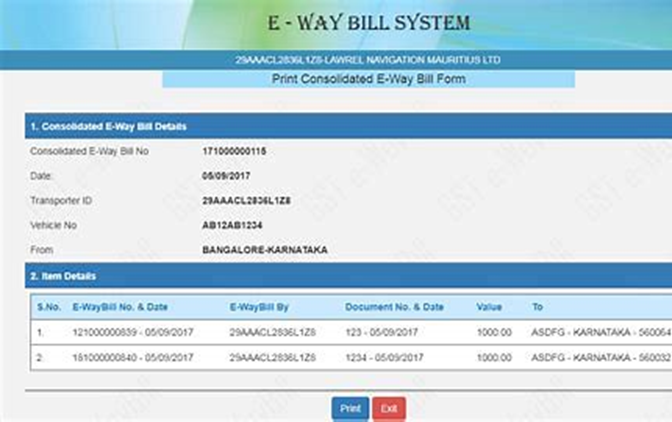
- Transporters handling multiple consignments in a single conveyance have the option to streamline the E-Way Bill generation process through the use of the form GST EWB-02. This form also allows the generation of a consolidated E-Way Bill by providing the E-Way Bill numbers of each consignment. Adopting this approach simplifies the documentation process for transporters and enhances the overall efficiency of managing multiple consignments within a single conveyance.
Source: Support.tax.aj.com
Proactive Steps for E-Waybill Compliance
- Proactive engagement with unregistered transporters is pivotal for seamless E-Waybill compliance. Encouraging and facilitating the continuous enrollment of unregistered transporters on the E-Way Bill portal ensures that businesses have a pool of authorized and compliant transporters. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of last-minute complications and promotes a culture of adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Given the dynamic nature of goods transportation, businesses must prioritize the timely updating of vehicle details. Recent updates allowing for the expression of the mode of transport as ‘Ship/Road cum Ship’ present an opportunity for businesses to enhance the accuracy and relevance of vehicle details. This flexibility in updating information ensures that the E-Way Bill remains reflective of the actual transportation modalities, whether initially moved by road or ship.
- When faced with the scenario of multiple invoices for the same customer to be supplied through the same truck, a strategic approach is crucial. Businesses should evaluate the efficiency and compliance implications of generating multiple E-Way Bills versus consolidating them into a single bill. This decision-making process should be based on a thorough understanding of logistics, regulatory requirements, and the goal of ensuring accuracy in E-Way Bill documentation.
- Navigating the complexities of E-Way Bill generation when goods from a single invoice are moved in multiple vehicles requires an efficient and cohesive approach. Businesses should implement streamlined processes that facilitate the accurate generation of E-Way Bills for each vehicle while maintaining coherence across the entire consignment. Leveraging technology and automation can enhance the efficiency of handling such scenarios, ensuring compliance without compromising on accuracy.
- The suspension of GSTIN can disrupt the regular flow of E-Way Bill generation. Businesses should be proactive in adapting their processes to account for this situation. Clear communication with relevant stakeholders, including suppliers and transporters, is essential to prevent any disruptions. Understanding the constraints of a suspended GSTIN and adjusting internal processes helps businesses navigate this challenge smoothly.
- For transporters managing multiple consignments in a single conveyance, the option to generate consolidated E-Way Bills through form GST EWB-02 offers operational efficiency. Providing E-Way Bill numbers for each consignment allows transporters to streamline documentation and reduce the administrative burden. This consolidated approach aligns with the regulatory framework while optimizing the logistics of handling multiple shipments simultaneously.
Also Read: E-Way Bill For Job Work: Understanding The Compliance Requirements
Lessons Learned and Future Considerations
The practical issues and solutions discussed underscore the evolving nature of E-Waybill compliance. Businesses have gained valuable insights from navigating these complexities, highlighting the importance of adaptability, proactive measures, and understanding entity-specific challenges. As businesses move forward, it becomes imperative to consider the following:
i. Leveraging technology for seamless E-Waybill compliance is an ongoing consideration. Integrating systems that automate data entry, verification processes, and E-Way Bill generation enhances accuracy and efficiency. Businesses should explore technological solutions that align with the specific requirements of E-Waybill compliance.
ii. Given the interconnected nature of the supply chain, a collaborative approach with suppliers, transporters, and other stakeholders is essential. Clear communication, shared understanding of compliance requirements, and collaborative problem-solving contribute to a more resilient and efficient E-Waybill ecosystem.
iii. The dynamic nature of regulatory frameworks necessitates continuous training and updates for the personnel involved in E-Waybill compliance. Keeping abreast of the latest guidelines, procedural changes, and technological updates ensures that businesses operate within the current regulatory landscape.
iv. As businesses encounter diverse scenarios in E-Waybill compliance, developing scenario-specific protocols becomes crucial. Predefined processes for scenarios like multiple invoices or goods in multiple vehicles boost efficiency and minimize errors.
Summary
To quickly summarize, ensuring there is seamless E-Waybill compliance requires businesses. To navigate regulatory intricacies, adopt technological innovations, and maintain collaborative relationships within the supply chain.
The emphasis on a valid transporter ID and accurate vehicle details is not just a regulatory requirement; It is essential for businesses to optimize logistics, ensure legal compliance, and uphold the integrity of the taxation system.
Lessons from practical scenarios and proactive steps guide businesses navigating the dynamic E-Waybill compliance landscape.
Also Read: How Can I Extend The E-Way Bill Validity With Ease?
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an E-Way Bill, and when is it mandatory?
Specifically, an E-Way Bill is a document required for the movement of goods exceeding Rs. 50,000 in value under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime.
2. Who is responsible for E-Way Bill generation?
The primary responsibility lies with the seller or consignor. However, the transporter can initiate the process if the seller fails to do so.
3. What information is needed for E-Way Bill generation?
Additionally, the consigner requires the invoice, bill of supply, or delivery challan, along with the transporter’s ID, vehicle number, transport document number, and date.
4. Why is a valid transporter ID and accurate vehicle information crucial?
It not only prevents legal issues but also ensures GST compliance, avoids penalties, facilitates smooth transport, prevents misuse, enables tracking, and ensures accurate taxation.
5. What legal repercussions can arise from non-compliance with GST laws?
Moreover, non-compliance can lead to severe legal consequences, including hefty penalties and fines. Therefore, accurate documentation, including transporter ID and vehicle details, is vital to avoid legal challenges.
6. How does E-Way Bill accuracy facilitate smooth transportation?
Additionally, accurate information about the transporter’s ID and vehicle details is fundamental for the seamless movement of goods, ensuring efficiency and compliance. Also, preventing delays at checkpoints and tolls.
7. How does the E-Way Bill system prevent the misuse of goods transportation?
Furthermore, accurate transporter ID and vehicle details safeguard against unauthorized exploitation of the E-Way Bill system, ensuring compliance and security.”
8. Why is real-time tracking important in the E-Way Bill system?
Real-time tracking, which depends on accurate vehicle information, enhances transparency and provides valuable insights into shipment status. This is especially crucial for time-sensitive deliveries.
9. How does E-Way Bill accuracy contribute to correct taxation?
Accurate information in the E-Way Bill is essential for tax authorities to verify the legitimacy of goods in transit. Any discrepancy can, therefore, lead to errors in tax calculations and potential compliance issues.
10. What are some practical issues in E-Way Bill processes and their solutions?
Challenges include handling multiple invoices, goods movement in multiple vehicles, unregistered transporters, suspended GSTIN, and consolidating E-Way Bills. Also, Solutions involve strategic decision-making, efficient handling of unique scenarios, proactive steps, and technological integration.

