Introduction
Businesses often make deals with suppliers to get the things they need for their daily operations. This could be buying a service or product. But sometimes, there’s a problem with what the supplier provides. When this happens, the business decides to return the defective product to the supplier. This is called a purchase return.
When a purchase return takes place the business need to make changes in the journal entries. It can impact the overall financial statements. In this blog, we’ll dive into the details of purchase returns, their processes, importance, and more. Understanding how to handle purchase returns efficiently is vital for businesses to maintain accurate financial records and make informed decisions. So, let’s explore the intricacies of purchase returns and how they affect a company’s financial health.
Basics of Purchase Returns
Purchase returns, also known as returns outwards or returns to suppliers, are transactions where a business returns goods previously purchased from a supplier. Understanding the basics of purchase returns is essential for maintaining accurate accounting records and ensuring proper financial management within a company.
So, in simple words, A purchase return refers to the process of returning merchandise or goods to a supplier due to various reasons such as defects, incorrect quantity, damaged goods upon receipt, or simply an overstock situation.
There could be various reasons but few common reasons are damaged goods, wrong style, size or color, late delivery, wrong product or it can be a change of mind. Usually the purchase return happens in these reasons.
Also Read: How To Create A GST Ready Purchase Invoice
Purchase Return Process
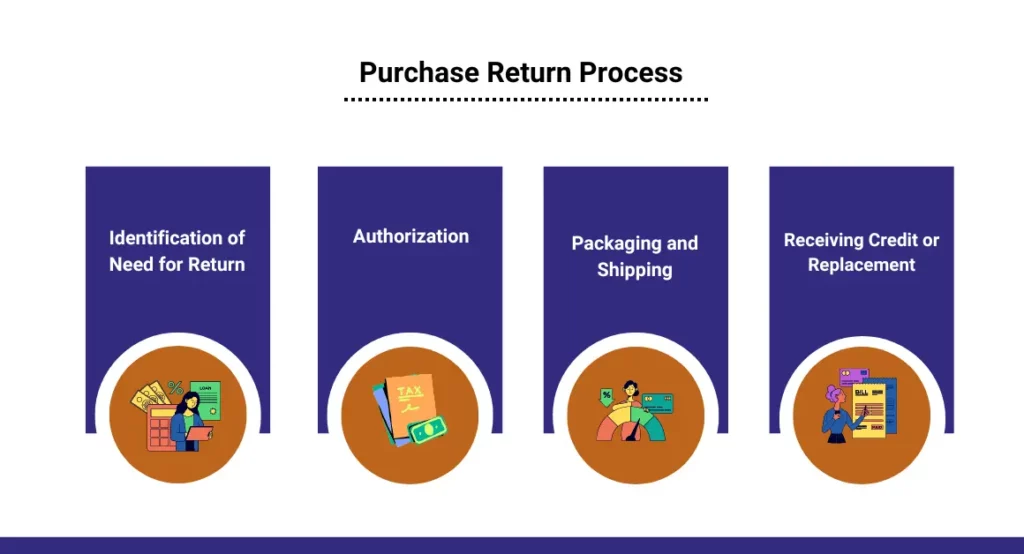
The purchase return process, also known as the returns outwards process, involves returning goods to a supplier for various reasons such as defects, wrong quantity, damaged items, or overstock situations. This process is crucial for businesses to maintain accurate inventory records, manage costs, and uphold quality standards. Here’s an explanation of the typical steps involved in the purchase return process:
1. Identification of Need for Return
The purchase return process usually begins when a company identifies the need to return goods to a supplier. This could be due to several reasons like Defective Goods, Incorrect Quantity, Damaged Goods, Overstock or Excess Inventory: When a company has ordered more than it can sell or store, it might return excess items to the supplier.
2. Authorization
Before returning the goods, it’s common practice for the company to contact the supplier and request authorization for the return. This step is crucial as it ensures that the supplier is expecting the return and can process it efficiently.
3. Packaging and Shipping
Once authorization is obtained, the goods are packaged securely for return shipment. It’s essential to follow the supplier’s instructions for packaging and shipping to ensure the return is accepted without issues.
- Packaging: Goods should be carefully packed to prevent further damage during transit. The packaging should also include any necessary documentation such as a copy of the purchase order and the return authorization.
- Shipping: The goods are then shipped back to the supplier using the agreed-upon shipping method. The company might use its preferred shipping carrier or follow specific guidelines provided by the supplier.
4. Receiving Credit or Replacement
After the supplier receives the returned goods, they will inspect the items to ensure they are in the expected condition. Depending on the supplier’s policy and the reason for the return, the following outcomes are possible:
- Credit Note: If the return is accepted, the supplier issues a credit note to the company. This credit note represents a reduction in the amount owed by the company to the supplier. The company can then use this credit note to adjust its accounts payable balance with the supplier.
- Replacement Goods: In some cases, especially when the return is due to defects or damages, the supplier might provide replacement goods instead of issuing a credit note.
Importance of Accurate Journal Entries
The importance of accurate journal entries can be explained in simple terms as follows:
Importance of Accurate Journal Entries
-
Keeping Track of Money:
- Think of journal entries as a diary for a company’s money. Accurate entries help a business know exactly where its money is coming from and where it’s going.
-
Making Smart Decisions:
- When the entries are correct, business owners can make smart decisions about spending and saving. It’s like having a clear map to follow.
-
Paying Bills and Employees:
- Accurate entries ensure that bills get paid on time and employees get their salaries. It keeps everything running smoothly.
-
Showing How Well the Business is Doing:
- When the entries are accurate, it’s easier to see if the business is making a profit or if it needs to adjust things. It’s like keeping score in a game.
-
Following the Rules:
- Governments and tax authorities need accurate entries to make sure businesses are following the rules. It’s like playing by the rules in a game to avoid penalties.
-
Helping in Tough Times:
- During tough times, accurate entries can show where a business might need to cut costs or find new ways to make money. It’s like having a roadmap during a storm.
Also Read: Accounting Entries – Purchase Entries With GST In The Accounting Journal
Components of a Purchase Return Journal Entry
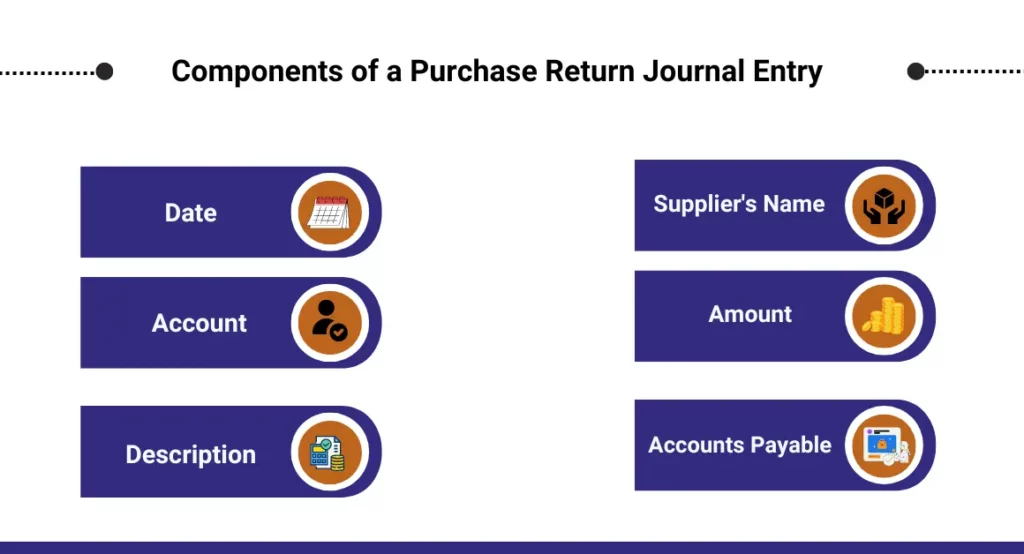
Let’s break down the components of a purchase return journal entry in simple terms:
-
Date:
- This is the day when the return is happening. Just like writing the date on a letter, it helps to know when this transaction took place.
-
Account:
- Think of this as the category or type of money involved. In a purchase return, the main account used is “Purchase Returns” or “Returns Outwards.” It’s like sorting money into different jars for easy tracking.
-
Description:
- Here, a brief explanation of the return is written. It’s like a small note to remind why the return is happening, such as “Returned defective goods to ABC Supplier.”
-
Supplier’s Name:
- This is the name of the company or person the goods are being returned to. It’s like addressing an envelope to make sure it goes to the right place.
-
Amount:
- The amount of money being returned is recorded here. This is usually the cost of the returned goods. It’s like writing down how much is going back in the “money jar.”
-
Accounts Payable (if applicable):
- If the company owes money to the supplier for the returned goods, this account is used. It’s like marking that the company has less money to pay because of the return.
In simple terms, a purchase return journal entry is like a note that says:
“On April 9, 2024, we returned some defective goods worth $500 to ABC Supplier.” It helps the business keep track of returned items and the money involved.
Example of purchase return journal entries
Let’s say a company, ABC Electronics, purchased electronic components worth ₹10,000 from XYZ Electronics but later found that some of the components were damaged upon delivery. As a result, ABC Electronics decided to return these damaged components to XYZ Electronics.
Date: April 9, 2024
- Account: Purchase Returns (where returned items are recorded)
- Description: Returned damaged electronic components
- Supplier’s Name: XYZ Electronics (who the goods are being returned to)
- Amount: ₹2,000 (the value of the returned damaged components)
- Accounts Payable (if applicable): If the company owes money to XYZ Electronics for the returned goods, it would be listed here.
| Date | Account | Description | Supplier’s Name | Amount | Accounts Payable |
| 2024-04-09 | Purchase Returns | Returned damaged electronic components | XYZ Electronics | ₹2,000 |
Explanation:
- Date: April 9, 2024
- Account: Purchase Returns (where returned items are recorded)
- Description: Returned damaged electronic components
- Supplier’s Name: XYZ Electronics (the supplier from whom the goods were purchased)
- Amount: ₹2,000 (the value of the returned damaged components)
Impact of Financial Statement
Here’s a simple explanation of the impact of purchase returns on financial statements:
Impact on Financial Statements
-
Income Statement:
- Revenue: Purchase returns reduce the company’s revenue. If a company had previously recorded the sale of goods that are later returned, the revenue from that sale will be reduced.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): When goods are returned, their cost is subtracted from the COGS. This reduces the COGS, which can increase the gross profit margin.
-
Balance Sheet:
- Accounts Payable: If the company has not yet paid for the returned goods, the accounts payable balance is reduced. This means the company owes less money to suppliers.
- Inventory: The inventory balance decreases because the returned goods are no longer in stock. This affects the asset side of the balance sheet.
-
Cash Flow Statement:
- Operating Activities: Purchase returns are reflected in the operating activities section. If the return involves a cash refund, it would be shown as a decrease in cash from operating activities.
-
Profitability Ratios:
- Gross Profit Margin: With reduced COGS due to returns, the gross profit margin may increase. This ratio indicates how efficiently a company is producing goods.
Also Read: Is Tax Included in Purchase Orders?
FAQ’s
-
What are purchase returns, and why do they occur?
Purchase returns refer to the process of returning goods to a supplier due to various reasons such as defects, incorrect quantity, or damaged items. They occur when a company needs to reverse a purchase transaction.
-
How does the purchase return process work?
The purchase return process typically involves identifying the need for a return, obtaining authorization from the supplier, packaging and shipping the goods back, and receiving credit or replacement from the supplier.
-
Why is accurate recording of purchase return journal entries important?
Accurate journal entries ensure that the company’s financial records reflect the true nature of the purchase return transactions. This is crucial for maintaining transparency, making informed decisions, and adhering to accounting standards.
-
What are the components of a purchase return journal entry?
A purchase return journal entry includes the date of the return, the account (such as “Purchase Returns”), a description of the returned items, the supplier’s name, the amount of the return, and the accounts payable if applicable.
-
Can you provide an example of a purchase return journal entry?
Certainly! Here’s an example:
| Date | Account | Description | Supplier’s Name | Amount | Accounts Payable |
| 2024-04-09 | Purchase Returns | Returned damaged items | ABC Supplier | $500 |
-
How do purchase return journal entries impact financial statements?
Purchase return journal entries impact financial statements by reducing revenue, lowering cost of goods sold (COGS), decreasing accounts payable, affecting inventory balances, and potentially influencing profitability ratios.
-
What is the significance of maintaining accurate purchase return records?
Accurate purchase return records help businesses track inventory, manage costs effectively, improve supplier relationships, ensure compliance with accounting standards, and make informed financial decisions.
-
How do purchase return entries affect the gross profit margin?
Purchase return entries can potentially increase the gross profit margin. When COGS decreases due to returns, the gross profit margin improves, indicating better efficiency in producing goods.
-
Is it necessary to document the reason for each purchase return?
Yes, it’s important to document the reason for each purchase return. This helps in understanding trends, identifying recurring issues, and providing a clear audit trail for accounting purposes.
-
What steps can a company take to improve its purchase return process?
Companies can improve their purchase return process by implementing clear policies and procedures, training staff on proper return handling, promptly communicating with suppliers, conducting regular audits, and leveraging technology for efficient tracking.

