Introduction
GST compliance is crucial for registered taxpayers in India. The government has launched the GST portal to streamline taxation monitoring and created a unified GST taxation system. As per the new GST act, you must pay GST instead of different types of direct and indirect taxes. This eliminated the cascading tax burden on taxpayers and improved tax collection.
The tax authorities have created new rules for GSTR-1 filing, requiring business owners to file tax returns monthly, quarterly, and annually. Regardless, you must pay only one GST tax for a taxable supply of goods and services. The newer system is simplified, but it involves different types of standardised forms.
GSTR 1 is a monthly or quarterly return statement of outward supplies of goods and services. We are committed to helping you understand GSTR 1 filling and return filing through this blog.
Decoding GSTR-1 Form
Every GST-registered taxpayer must file a GSTR 1 return monthly or quarterly. Businesses with an aggregate annual turnover of less than Rs.5 crores registered under the QRMP scheme can file GSTR 1 quarterly. All other types of taxpayers must file it monthly. Even if there are no sales transactions during the tax period, you must file a nil GSTR.
Registered persons exempted from filing GSTR 1 are:
- Suppliers of Online Information and Database Access or Retrieval (OIDAR)
- Input service distributor
- Non-resident taxpayer
- Taxpayer under composition scheme
- Liable to collect TCS or deduct TDS
The due date for the monthly filing of GSTR 1 is the 11th of the next month, and the quarterly filing is the 13th of the month following the quarter. In certain cases, exemption may be provided, and the government will announce it. Otherwise, the due date must be followed strictly.
Source – https://www.shutterstock.com/shutterstock/photos/2057889671/display_1500/stock-vector-gst-compliance-return-filing-process-illustration-as-eps-file-2057889671.jpg
The GSTR 1 is the backbone for return filing in the GST ecosystem. Once the return is filed, you cannot change the form. You can only make amendments in the subsequent GSTR 1 return forms. Amendments in the GSTR 1 form must be made within 30th November for the financial year.
The form GSTR 1 includes:
- Invoice-wise details – Corresponding to inter-state and intra-state supplies to registered persons and inter-state supplies made to unregistered persons with invoice value exceeding Rs. 2.5 lakh.
- Consolidated details – Corresponding to intra-state supplies and inter-state supplies made to unregistered persons
- Debit and credit notes – Issued during the tax invoice for previously issued invoices
- Amendments – Corresponding to previous GSTR 1 return forms.
After filing GSTR 1, the GST portal auto-populates GSTR 2A, GSTR 3B, GSTR 4A, and GSTRA 6A of registered customers based on the supplier details.
Also Read: Overview And Purpose Of GSTR-1
Obligations and Responsibilities
Registered persons have numerous obligations and responsibilities while filling out GSTR 1 forms. They must report all the details accurately. The GSTR 1 details are crucial for calculating tax liabilities. However, GSTR 1 serves far greater purposes as well.
The GSTR 1 data is used for auto-populating GSTR 2A and GSTR 3B, which buyers use to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC). If the GSTR 1 you filed is incorrect, your customer cannot claim the ITC they are entitled to. Therefore, to establish strong business relationships, you must make it easier for your customers to claim their ITC with accurate GST reporting.
Filing monthly or quarterly GSTR 1 is the first step towards GST compliance. Late filing of GSTR 1 will result in late filing of the rest of the GST forms because you cannot file a return form unless you have filed all the previous return forms.
Key Components of Outward Supplies
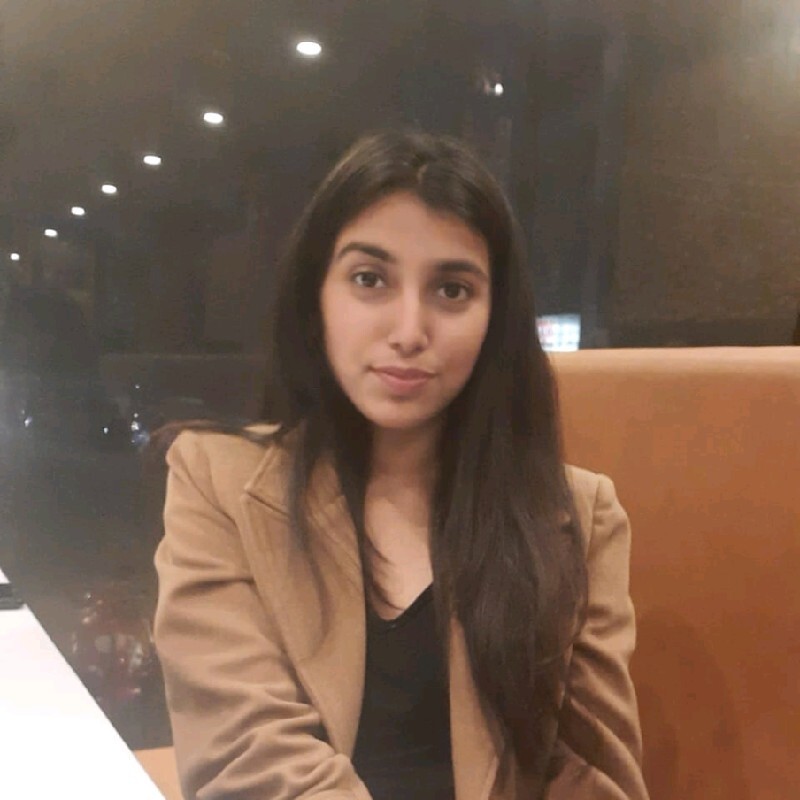
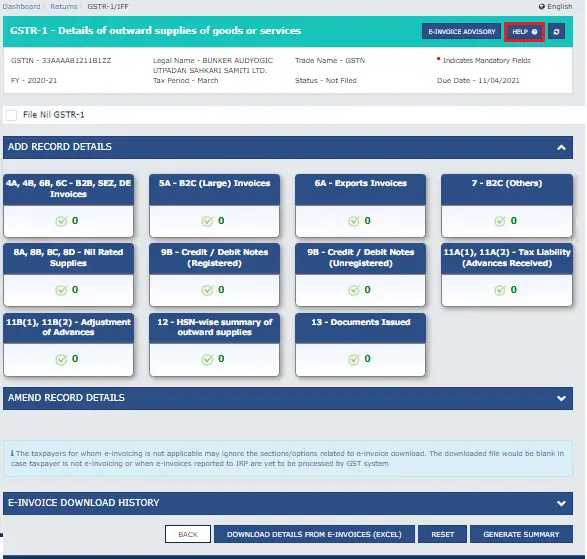
The GSTR 1 return filing can be done only electronically. The government has simplified and streamlined the entire process. The summary and invoice details of outward supplies must be entered in one of the 13 tables. You can enter new invoice details in the following tables:
- 4A, 4B, 6B, 6C for B2B, SEZ, DE invoices
- 5A for large B2C invoices
- 6A for export invoices
- 7 for B2C invoices
- 8A, 8B, 8C, and 8D for Nil rated supplies
- 9B for credit or debit notes associated with registered customers
- 9B for credit or debit notes associated with unregistered customers
- 11A(1), 11A(2) for tax liability advances details
- 11B(1), 11B(2) for adjustment of advances
- 12 for HSN-wise summary
- 13 for documents issued
If you have made mistakes in the previous GSTR 1 form, you can make amendments in the following sections:
- 9A for amended B2B, B2C, and exports invoices
- 9C for amended credit or debit notes associated with registered and unregistered customers
- 10 for amended B2C invoices
- 11A for amended advances received
- 11B for amended adjustment of advances
You must take utmost care in ensuring that invoice details are filled correctly in each section. Errors in GSTR 1 will be transferred to other GST forms, which can trigger GST audits.
In-depth Analysis of Data to Be Furnished
The GSTR 1 form is a mix of summarised and granular details. In some sections, you must enter GSTIN, invoice number, taxable value, state of supply, etc., while it is sufficient to mention the total taxable value in other tables. Let’s understand this requirement in detail.
- Table 4 – Must enter GSTIN, UIN of the recipient, invoice number, date and value, GST rate, taxable value, tax amount (categorised as central tax, state tax, and integrated tax), and place of supply (PoS). The subtables 4A, 4B, and 4C must be filled out with invoice details.
- Table 5 – Must enter the invoice number, date, value, GST rate, taxable value, tax amount (categorised as central tax, state tax, and integrated tax), and place of supply (PoS). The subtables 5A and 5B must be filled out with invoice details.
- Table 6 – Must enter the GSTIN of the recipient, invoice number, date and value, GST rate, taxable value, tax amount of integrated tax, and Shipping bill/Bill of export number. The subtables 6A, 6B, and 6C must be filled out with invoice details. If the shipping bill details are unavailable when filing the GSTR 1 return, table 6 will still accept the entered details. When the shipping bill details become available, you can add them as amendments in Table 9 at that tax period with a detailed 13-digit code, including the six-digit port code. As recipient GSTIN is irrelevant in export transactions, it can be left blank. For Zero-rated supply transactions executed without integrated tax or Letter of Undertaking (LUT), you can report the tax amount as ‘0’ in tables 6A and 6B.
- Table 7 – Must enter consolidated details such as total taxable value and amount of CGST, SGST, IGST, or UGST tax. There is no need to fill in invoice details. In subtables 7A (1 and 2) and 7B (1 and 2), you must enter gross supply details for inter-state and intra-state supplies corresponding to B2C transactions. You must remember to enter the GSTIN number of the ecommerce operator.
- Table 8 – Must enter the value of nil-rated, non-GST, and exempt supplies.
- Table 9 – Must enter original information of credit and debit notes in the earlier tax period, including invoice details and details of a revised version of debit and credit notes in the first three columns. You need to enter PoS only if it differs from the original invoice. Add shipping bill details for export transactions only if amendments are necessary.
- Table 10 – Must enter amendments for details listed in Table 7 in the earlier tax period.
- Table 11 – Must enter advance details, tax amount paid on advances, and PoS. You must fill in 11B if you received advances in the earlier tax period, but furnish the invoice only in this tax period and adjust advances against supplies now.
- Table 12 – Must enter HSN code summary details.
- Table 13 – It is a crucial table where you must upload all the documents for which details and summaries are furnished in the tax period. Documents include:
- Invoices
- Debit note
- Credit note
- Receipt voucher
- Payment voucher
- Refund voucher
- Deliver challan issued, cancelled
The number of invoices reported in Tables 4,5 and 6 must match the number of invoices uploaded in Table 13.
Exploring Amendments and Corrections
It is common to make corrections while entering financial information. That is why GSTN has facilitated you to change the GSTR 1 form. However, you must clearly mention these corrections in the exclusive amendments section.
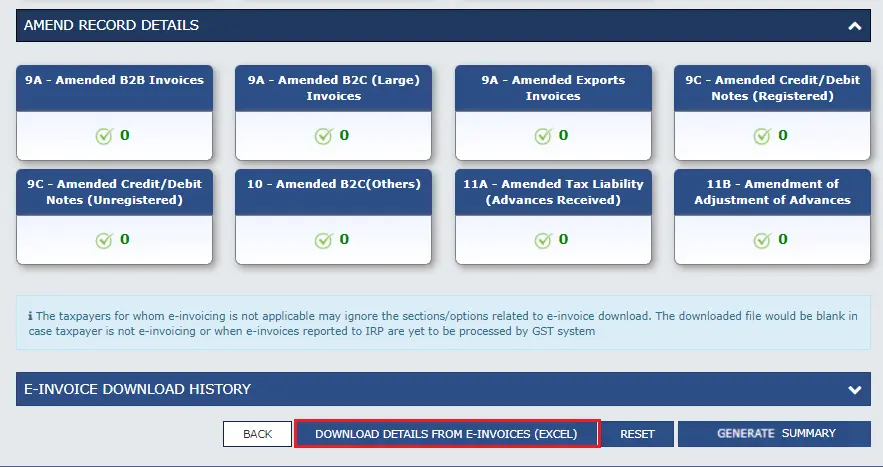
You can enter amendments only in tables 9, 10 and 11. Details of debit notes, credit notes, and refund vouchers issued for amendments must be present in these tables. All changes related to B2B supplies, large B2C supplies, export supplies, deemed exports, and exports to SEZ units or developers must be added in the appropriate sections.
While entering amendment details, you must also enter the original invoice details corresponding to the latest corrections. The tax authorities will verify this data before adjusting your tax liabilities accordingly.
Also Read: Amendments and Revisions in GSTR-1
Leveraging Technology for GSTR-1 Filing
Amendments become essential for GSTR-1 filing, especially when the shipping bill is not available in the current tax period, or you received only advances in the current tax period. However, adding amendments for entering wrong invoice details is not advisable. Making frequent mistakes in GST return filing can also alert authorities and trigger audits.
Therefore, you must leverage technology to file GSTR 1 accurately without errors and mistakes. Using automated billing software like CaptainBiz can make this process hassle-free. The software automatically fills out the GSTR 1 table details from the generated invoices. As this tool generates only GST-compliant invoices, you can rest assured that your GSTR 1A filing will be accurate and current.
Reconciliation and Verification Process
The data from GSTR 1A forms the basis of other GSTR forms like 2A, 3B, etc. Therefore, reconciliation and verification are crucial before filing a GSTR 1 return. Some of the reconciliations necessary are:
- Sales register vs general ledger
- Sales register vs EWB
- IRP e-invoices vs GSTR 1 data
- B2C invoices/non e-invoices vs GSTR 1 data
Impact of GSTR-1 on Businesses
All the documents related to the current tax period must be promptly included in the GSTR 1 return filing process. Reconciliation will help you ensure that there are no discrepancies that can result in penalties and charges. Accurate reporting of taxable amounts is crucial for GST compliance. Paying the correct tax throughout the financial year will help your business build a reputation.
GSTR 1 accuracy will impact your business and your customer’s business. Your GSTR 1 return filing forms the basis of the ITC claiming of your recipients. If you have reported invoices with mistakes and errors, your recipients cannot claim ITC, and their tax liability will increase.
Also, proper management of GST invoice filing will give detailed sales insight so that you can devise new strategies to focus on large invoices and increase sales.
Also Read: Is GSTR 1 Not A Return? Understanding The Intricacies Of GST Filing
Conclusion
GSTR 1 return filing requires processing a large amount of data and entering the data in the correct columns in the GST portal. This can become a daunting process when you deal with thousands of invoices every month. Reconciliation complexity will also increase by importing invoice data, converting it into the right format for comparison, and matching details to identify missing information. All these monotonous processes can be automated using AI-powered billing tools that can create GSTR 1 reports with a single click.
CaptainBiz is a cloud-based AI-powered GST billing software that can automate GST compliance for your business. Manage all types of business transactions from a single window to stay organised and improve business cash flow. Get access to a 14-day free trial to streamline GST return filing.
FAQs
-
Who needs to file GSTR 1?
All casual and normal taxpayers registered under GST must file GSTR 1. The exemptions are Input Service Distributors, non-resident taxable persons, persons paying tax under composition levy, persons liable to collect TCS or deduct TDS, and online information and database access or retrieval (OIDAR) services suppliers.
-
Do I have to include detailed information in GSTR 1?
Yes, you must include all details about outward supplies, including invoice numbers, date, supply value, taxable value, tax amount, etc. Documents related to invoice details must also be uploaded to the GST portal.
-
Can I file GSTR 1 offline?
No, GSTR-1 filing can only be done electronically. However, you can enter GSTR 1 details offline. A GST report generation tool will help you create GSTR 1 data and convert it into JSON format offline. You must upload this JSON file to the GST portal and file your return online.
-
Do I need computer proficiency to file GSTR 1?
Yes, basic computer proficiency is expected to fill GSTR 1 details correctly and file the tax return. However, there is no need for a dedicated auditor because you can manage GST filing on your own with an efficient GST billing solution like CaptainBiz.
-
What happens if I don’t file GSTR 1 before the due date?
Failing to file a GSTR 1 return before the due date will incur late fees and penalties. You cannot file returns for a tax period if you have not filed returns for the previous tax periods. So, the late fees and penalties will cascade and increase tax liabilities due to the late filing of GST 1.
-
Can I revise GSTR 1 before filing?
Yes, you can make changes to GSTR 1 data before filing the return for the tax period.
-
Do I need to upload every single invoice to GSTR 1 individually?
You must report every invoice in the GSTR 1 form for the current tax period. However, you need not upload invoices one by one. You can use a bulk uploading tool to upload invoices in bulk. The best way is to use automated software that automatically uploads GSTR 1 every time you create a GST invoice.
-
What can I do if I file GSTR 1 with the wrong invoices?
To avoid mistakes and errors, reconciling GSTR 1 data before filing the return is crucial. However, if you find discrepancies in the data after filing the return, you must make amendments in the subsequent GSTR 1 filing. Allowing errors to trickle down will make reconciling during annual return filing harder.
-
Will my GSTR 1 return filing affect my customer’s GST return filing?
Yes, your GSTR 1 data will auto-populate your customers’ GST forms. Your outward supplies data is essential for them to report their purchases and claim ITC.
-
What can I do if I have no outward supplies for the tax period?
If there are no outward supplies for the tax period, you must file a nil GSTR 1 report. You cannot avoid filing GSTR 1 in any case. Nil reports can now be filed using SMS without accessing the GST portal.

