The introduction of GST caused a major reform in the indirect tax system in India. It benefited thousands of businesses, especially small and medium businesses. But there have been instances of fraud where innocent customers and the government have been tricked. The most common of these frauds include charging more tax, charging tax on tax-free products, and also cheating small traders and businesses by posing as GST officials. Most common people are not aware of the rates of GST applicable, which has led shopkeepers, restaurants, and other business enterprises to illegally charge higher rates of GST than specified under the law. They charge a high amount of tax on products and services from customers but do not pay or remit them to the government. All these are instances of fraud and need to be reported to the authorities. Here we discuss in detail the types of fraud and the process to file a complaint against GST fraud.
Types of GST fraud
- Collecting GST on tax-free products: There are various items on the GST-exempted list on which the traders are not supposed to levy tax. For example, we need items like mineral water, grains, milk, vegetables, milk, etc. The complete list can be found on the GST website. As most people are not aware of this, the shopkeepers and dealers charge and collect the tax from the customers but never pay it to the government.
- Collecting GST on products and services that have already paid VAT, or charging GST in addition to VAT: After the implementation of GST, VAT and service tax have been replaced by the new tax system. But some businesses, like restaurants, are still charging VAT, and some are charging GST along with VAT. This is a typical example of fraud. The businesses are supposed to clear the taxes on their old stock and implement the new GST system immediately.
- Charging more GST than the rate defined in GST: Traders often charge more than applicable as most people are not aware of the specified rates. A common example is the GST charged on clothes. According to GST law, a 5% tax is applicable on clothing when its value is equal to or less than Rs.1000/-. But many shopkeepers are charging more than that.
- Fraudsters pretending to be GST officials: Many people have reported being approached by fake agents, claiming to be GST officers, demanding taxes. Whereas the commissioner of GST has clarified that no official is permitted to visit any trader or shopkeeper and demand money, GST is only evaluated during the transit period.
Actions against GST fraud
The GST Council has set up a grievance redressal portal for registering any type of GST fraud and other complaints. Customers and taxpayers can lodge their complaints or seek answers to their GST-related issues on this portal.
GST complaint portal and how it works
The portal is user-friendly and helps individuals lodge their complaints and raise tickets by themselves. They can also check the status of the complaint and its progress.
How to report GST fraud
There are many ways a person can file a GST-related complaint about any illegal charges or fraud. They are:
Step 1: The first step is for the person to go to the GST portal at https://www.gst.gov.in/
Step 2: Then scroll down and click on the ‘grievance redressal portal of GST.’

Step 3: The portal will redirect the user to a new page.
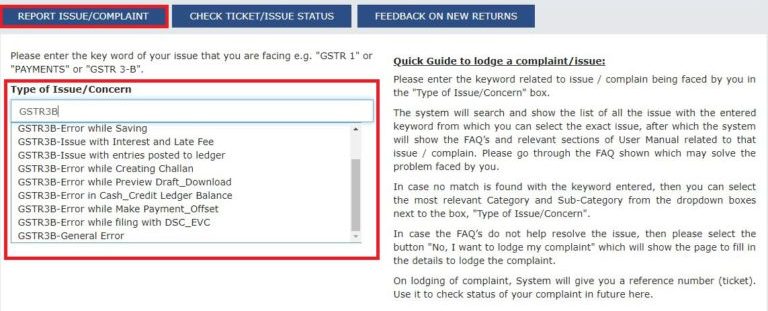
Step 4: The user has to click on ‘Report Issue’ and lodge the type of issue or concern.
Call the toll-free number of the GST complaint portal. The number is 1800-103-4786. After registering, the user will get an acknowledgement number with a ticket number (TRN), which can be used to track the complaint status.
Fraud involving fake GST invoices
GST invoices are generated by a seller or supplier when goods and services are purchased. It has all the information, like the identification of the buyer, seller, name and description of the product, quantity, date of purchase, discount, etc.
A fake GST invoice is an invoice generated without the actual supply of goods and services or GST payment. Fake invoices are used for tax evasion, claiming credit, fake purchases, and money laundering.
Often, traders create fake invoices to claim tax credits. To avoid being a victim of such fraud, customers can do a quick check to check the authenticity of the bill they receive by following a few simple steps:
- Verify GSTIN: The first step is to verify the authenticity of the GST bill. Every registered supplier of goods and services is assigned a unique 15-digit number, which is a combination of state code, PAN, and a unique registration number.
- Visit the GST portal: To verify the GSTIN, the purchaser has to visit the GST portal at www.gst.gov.in. Then click on the ‘search taxpayer’ tab. There, enter the GSTIN of the supplier, and click on search. If the number is valid, the name and address of the supplier will be displayed on the screen.
- Check the invoice details: The next step is to check the invoice number and date that are reflected in the bill given by the trader. Any discrepancy in the invoice number or date shows that the bill is fake.
- Verify the invoice value and the tax amount: The bill should show the correct invoice value, including the tax amount at the correct applicable GST rate. The tax amount can be calculated by using the tax calculator provided in the portal.
- Check for the HSN/SAC code: The HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code is a unique code assigned to goods, and the SAC (Services Accounting Code) is a code assigned to services. The bill should mention the correct HSN/SAC code. It can be verified through the GST portal.
- Verify the signature of the supplier: The bill must contain the genuine signature of the supplier or his authorized signatory. This signature can be verified with the signature available on the portal.
- Check the tax payment status: The tax payment status of the supplier can be checked on the GST portal. If the tax is paid, it will be reflected in the GST return filed on the portal.
- Raise a complaint against GST fraud: To raise a complaint against a supplier for GST fraud, the customer has to visit the official portal of GST, then click on CBEC Mitra Helpdesk and ‘Raise Web Ticket’. They can also send an email to helpdesk@icegate.gov.in.
Customers can also call the helpline at 1800-1200-232.
Another method to complain is to access their official Twitter handle at @askGST_GoI and the finance ministry at @FinMinIndia and lodge a complaint there.
Conclusion
Identifying fraud at the initial stages is important because most of them have a tendency to operate in the names of dummy persons, making it difficult for the authorities to identify and punish them. So, customers, on their part, can take due diligence, be aware of the types of frauds possible under GST, and take steps to identify and report the fraud at the operational level and avoid losses to themselves and also to the government. Many facilities have been provided by the company to report fraud, and customers can easily avail of these with alertness and awareness.
Frequently asked questions
-
What are the risk indicators for fraudsters in GST?
Answer: Some of the risk indicators of fraudsters that the authorities need to monitor are:
- Multiple registrations under the same PAN
- Common mobile numbers, email addresses, authorized signatories, promoters, etc.
- Re-registration under GST of applicants who have been rejected before
- Registration under CGST of the PAN for which offense has been booked under SGST
-
How can a customer check the GST rate on the product before purchasing it?
Answer: Customers can check the applicable GST rate of the product online. The government has provided a ‘GST rate finder app’ online on the portal, which can be used to find the exact GST rate applicable to any item or service.
How To Activate a Suspended GST Number, What Are the Reasons for Suspension of GST Registration and How to Resolve it.
