INTRODUCTION
Navigating the intricacies of E-waybill extensions is crucial for seamless logistics management. Understanding the time limits and procedures involved in extending an E-waybill can significantly impact operational efficiency.
This comprehensive guide offers a step-by-step breakdown, shedding light on the essential aspects of extending E-waybills, ensuring businesses stay compliant and streamlined in their transportation endeavors.
Time limits for extending E-waybill validity
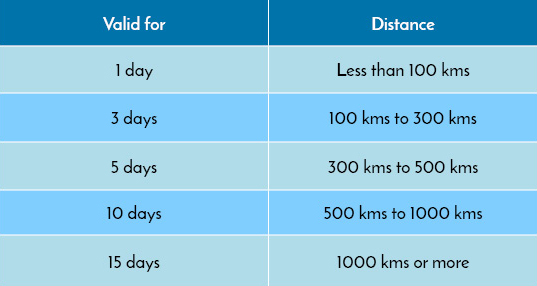
In India, the validity period for an E-waybill is determined by the distance to be covered during the transportation of goods. The general rule says, for every 100 kilometers or so, the E-waybill is valid for only 1 day. The maximum validity period is 15 days following the same rule.
Now, here is the easy calculation: if the transportation distance is less than or equal to 100 kilometers, the validity is 1 day. For distances between 101 and 200 kilometers, the validity is 2 days, and so on. This pattern continues until the distance reaches 1,000 kilometers or more, where the validity is capped at 15 days.
Step-by-step procedures for E-waybill extension
Look at the complete guide to extend an E-way bill’s validity after it expires:
- First, visit the official e-Way Bill portal.
- Enter your Username and Password to log in to the portal. Here, you will find a list containing invoices with details on E-way bills for the previous one-week period.
- Check the filters available on the e-way bill’s webpage for using the E-way bill validity filter. By doing so, you may filter the would-be-expiring e-way bills on the respective day. You may even select the option Expires Today in the validity filter to get information on e-way bills expiring on that day.
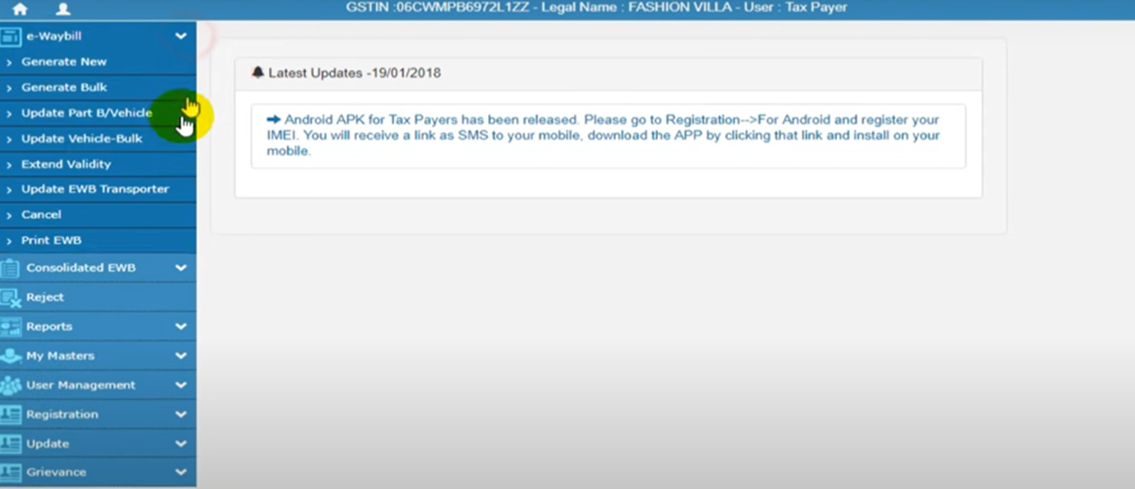
- Click on the “Extend Validity” option.
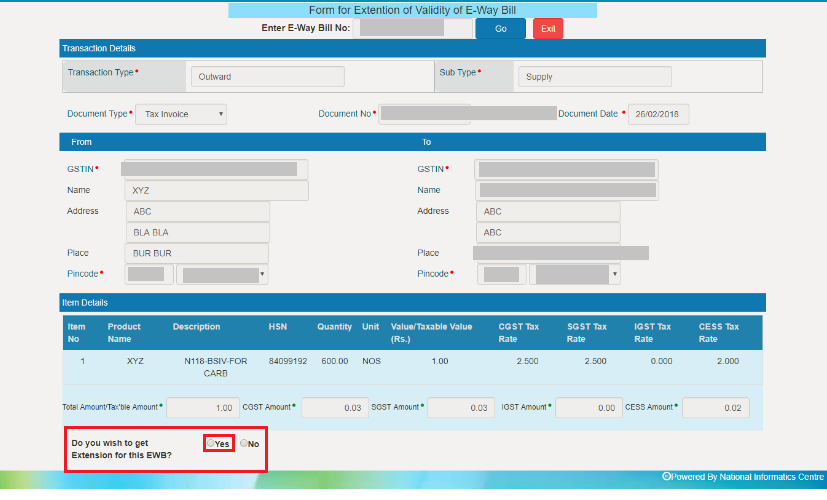
- After you trigger the extension of the e-way bill, you will get the prompt whether your chosen e-way bill is valid to extend. Besides, the user has to confirm to extend the validity of the e-way bill. The reason is that the website does not allow unnecessary e-way bill extensions.
- Enter the relevant details such as the reason for the extension and the approximate additional validity period needed.
- Review the details and click on the “Submit” button.
- If the e-Way Bill has already expired, you are required to pay a late fee to extend the validity.
- Once your request is approved, you can download and print the new e-Way Bill with extended validity.
- This is the way for extension of the E-way bill after expiry.
Also Read: Procedures and Documentation for Handling Expired E-waybills
Legal provisions defining time limits and procedures
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime of the Government of India looks after the legal provisions for extending E-waybill validity. Under Rule 138 of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Rules, 2017, an E-waybill can be extended by the person in charge of the conveyance for a further distance.
The reasons should be mentioned, whether it can be natural calamities, law and order issues, or any other exceptional circumstances.
It is advised to always check the official GST portal or consult with tax professionals for the most recent changes on E-waybill extensions in India. However, an E-waybill should stay compliant with the current regulations and be updated as per the latest notifications and amendments.
Compliance obligations in adhering to time limits
Compliance obligations in E-waybill extensions typically involve an attachment to regulations governing electronic documentation for the movement of goods. This includes accurate and complete information about the extended E-waybill, such as details about the consignment, transporter, and relevant tax invoices.
Additionally, businesses must stay updated about the latest changes in legislation related to E-waybills to maintain compliance with the evolving regulatory landscape. Regular audits and reviews of E-waybill processes are necessary to identify and rectify any non-compliance issues.
Documentation requirements for the extension process
To extend the E-waybill, you have to submit authentic documents and information to comply with the extension requirements. Here we present a complete list below:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reporting obligations for extended E-waybill procedures
The reporting obligations for extended E-waybill validity may vary from country to country. In India, the E-waybill system mandates the generation of these bills for the movement of goods exceeding a certain value or distance.
To change or extend the validity period, it’s crucial to comply with the reporting requirements set by the tax or transportation authorities. These might involve updating the system with the extended validity details, reasons for extension, and any necessary supporting documentation.
Always consult the official guidelines or reach out to the relevant authorities, such as the tax department or transportation regulatory bodies, for precise information on reporting obligations related to extended E-waybill validity in your specific area or country. Regulations may have been updated since my last information update, so staying current with the latest guidelines is essential.
Challenges in complying with time limits and procedures
While extending the E-waybill validity, you may face some challenges. Here is a detail about this:
| Data Integrity and Security |
|
| Technological Challenges |
|
| Unexpected Business Scenarios |
|
Also Read: Challenges and Solutions in Tracking and Managing E-waybill Expiry
Exemption considerations for specific cases
Below are some of the exemptions that are taken into consideration for specific cases:
|
|
|
|
|
Best practices for smooth E-waybill extension processes
The best practices to extend the E-waybills in a timely manner are explained below:
| Gather All Documents | At the time of extension, you may need to submit all relevant information required for extension, such as the original E-waybill number, transportation details, consignment details, and reasons for extension. So, keep all these handy. |
| Be Aware of the Validity Period | An E-waybill is valid for a certain number of days depending on the distance to be traveled. So, ensure you are aware of the validity period and the time of its expiry. |
| Start Processing Before Expiry | Initiate the process for E-waybill extension in advance well before the expiry date comes. Last-minute extensions might lead to delays or some penalties. |
| Document Verification | Submit all the supporting documents related to the extension request are accurate and up-to-date. This includes invoices, transport details, and any other necessary paperwork. |
| Keep A Follow-up and Stay Informed | Check the status of the extension request on a regular basis and keep yourself updated with any changes or amendments in E-waybill rules and regulations. |
| Always Use Authorized Portals | To extend the E-waybill, login to authorized government portals or apps designated for E-waybill generation and extension. This will safeguard you from any data theft. |
| Timely Submission | Submit the extension request well before the expiry of the current E-waybill. This allows ample time for processing and avoids any disruptions in the transportation process. |
| Maintain All The Records | Keep the records abreast of all E-waybill extensions and associated documentation for future reference. |
Audit and verification of adherence to time limits and procedures
Here are some audit and verification steps that are performed during an E-waybill extension:
- E-waybills are electronic documents that contain details of the goods with the details of the consignor and consignee, here audit and verification of E-waybills in government shipments play a crucial role in making the process transparent and compliant.
- During the audit process, government authorities review E-waybills to confirm the accuracy of information. This involves cross-referencing details of the consignor, consignee, goods description, the time period, and the valid reason for delay.
- Verification procedures may involve real-time tracking of shipments using GPS technology or other tracking systems to ensure the current location of goods and the valid reason for delay. Additionally, authorities may compare E-waybill data with other relevant documents, such as invoices and tax records, to verify the consistency of information across different channels.
- Ensuring the integrity of the E-waybill system is vital for preventing tax evasion, fraud, and unauthorized movement of goods. Regular audits and verifications contribute to a robust system that enhances the overall efficiency and trustworthiness of government shipments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can say that understanding the procedure and time limit for E-waybill extension is important to have seamless transportation. We hope that this guide will help you to continue the extension process efficiently while upholding regular compliance. So, stay informed and compliant to maintain your supply chain and operate effortlessly.
Also Read: E-waybill Extension: When and How to Extend an E-waybill Validity
Also Listen: How to create E-way Bill With CaptainBiz
FAQs
Q1. What is the time limit for the extension of the validity of E-way bills?
The Validity of EWB can be extended only by the current transporter. If the transporter is not assigned, then the generator can update. The validity of EWB can be extended between 8 hours before expiry time and 8 hours after expiry time.
Q2. How long is the time limit for E-way bill cancellation?
The time limit to cancel the E-way bill is within 24 hours of generating. Once canceled, it is illegal to use such E-way Bills.
Q3. What is the reason for the E-way bill extension?
One can extend the validity of the e-way bill, if the consignment is not reaching the destination within the validity period due to exceptional circumstances like natural calamity, law and order issues, trans-shipment delay, accident of conveyance, etc.
Q4. What is the validity of the E-way bill for 400 km?
Here is a detailed rule of validity period and distances:
| Distance | Validity Period |
| <100 KM | 1 DAYS |
| >100 – < 300 KM | 3 DAYS |
| >300-<500 KM | 5 DAYS |
| >500 – < 1000 KM | 10 DAYS |
| MORE THAN >1000 KM | 15 DAYS |
Q5. How do I generate an E-way bill limit?
A GST-registered person cannot transport goods over ₹50,000 without an E-way bill generated through ewaybillgst.gov.in. Additionally, E-way bills can be generated or canceled via SMS, Android Apps, or APIs.
Q6. Can a backdated E-way bill be generated?
An e-way bill has to be made before the movement of goods by road. That is to say, the time of generation of the E-Way bill is not linked to the invoice date. Thus, the E-way bill can be generated after the invoice date.
Q7. What happens if the e-way bill expires?
Generally, the GST Authorities, in such cases where the validity period of the E-way bill has expired, take action under section 129 of the CGST Act. They pass the order of detention and penalize accordingly.
Q8. What is the rule 55 of the E-way bill?
E-Way Bill – Under rule 55A under CGST Rules, an E-Way bill, bill of supply, or tax invoice is not required to be carried then a delivery challan is issued.
Q9. What is the rule 129 of the E-way bill?
Section 129(3) of the CGST Act allows for the detention and seizure of goods that are being transported without an e-way bill. The authorized officer, upon the observance of any discrepancy in the E-way bill or the absence of a valid E-way bill, has the right to detain the vehicle and seize the goods.
Q10. How do I extend my expired e-way bill?
After selecting the e-Way bill to be extended, click on ‘More Actions‘ -> ‘Update EWBs‘ -> ‘Extend Validity‘ option to trigger the extension flow.

