When it comes to fostering economic development, the generation of jobs, the elimination of poverty, and the promotion of equality, the role of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) becomes vital in every economy throughout the world. As an important part of economic development, the micro, small, and medium-sized enterprise sector promotes equitable distribution and inclusive growth.
The employment growth rate of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) is the highest, which has a beneficial impact on production and exports.
The major purpose of this article is to analyze the performance of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) and their contribution to the inclusive prosperity of India.
Over the course of the past 20 years, the Indian economy has shown remarkable performance; nevertheless, the benefits of this expansion have not been distributed in an equitable manner.
Using a wide range of measures, such as employment generation, regional industry distribution, and innovation, researchers have investigated the influence that micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) have on a variety of groups and the participation of women in India.
Based on the findings of the study, the micro, small, and medium-sized enterprise (MSME) sector makes a significant contribution to inclusive growth in India by providing large job opportunities, ensuring that industries are spread fairly, and encouraging women from backgrounds of disadvantage to engage in business ownership. “Make in India,” “Digital India,” and other government policies for MSMEs have opened up new opportunities for the micro, small, and medium-sized enterprise (MSME) sector to experience significant growth over the next ten years.
MSME Performance in India
- In India, micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) are among the most important foundations of our economy. There are currently more than 6 crore micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) operating in the country, which together offer more than 11 crore jobs to the people.
- The sector accounts for around fifty percent of India’s total exports and provides approximately 30% of the country’s gross domestic product.
- The history of our nation’s development demonstrates that micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) have protected our nation from a variety of shocks and challenges.
- In light of the significance of the micro, small, and medium-sized enterprise (MSME) sector in the nation, the following section will provide a comprehensive review of the value that it holds for the Indian economy.
How MSMEs Help India Grow Inclusively
Micro Small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) in India are driving equitable growth. This area needs to be running well for the nation to grow in a balanced manner. In the section that follows, we will present the importance of MSMEs in India’s inclusive growth, considering the following factors:
- The development of employment opportunities in both rural and urban areas.
- Distribution of industries by region, both within and across states and between urban and rural areas.
- Many different social and economic groups, including the Other Backward Class (OBC), Schedule Caste (SC), Schedule Tribe (ST), and others, are participating in entrepreneurship.
- Women’s participation in business ownership.
Importance of MSMEs
Economic development, job creation, and inclusive growth are all greatly impacted by micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs).
-
Creating Jobs
As the country’s second-largest employer (behind agriculture), the micro, small, and medium-sized enterprise (MSME) sector is noteworthy while requiring relatively little capital. There was an increase of 1,109.89 lakh jobs in India’s MSME sector between 2015 and 2016, according to the 73rd wave of the National Sample Survey. The percentage of people employed in this sector is 55.85% in urban regions and 44.85% in rural areas.
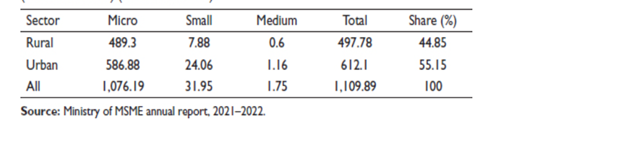
-
Industry Regionalization
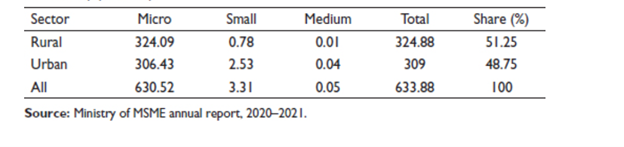
The MSME sector has a significant impact on the distribution of industries across different areas of India. While micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSME) span the nation, large-scale companies tend to cluster in a few states and major cities, erasing regional disparities in industrial growth. The data shows that whereas 51.25 percent of MSME units are located in rural areas, 48.75 percent are located in urban areas.
 Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in India are more evenly distributed throughout states than major corporations. In the fourth all-India MSME Census, the three states of Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Tamil Nadu accounted for closer to 31% of the total units; however, in the NSS 73rd cycle, they accounted for 36%.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in India are more evenly distributed throughout states than major corporations. In the fourth all-India MSME Census, the three states of Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Tamil Nadu accounted for closer to 31% of the total units; however, in the NSS 73rd cycle, they accounted for 36%.
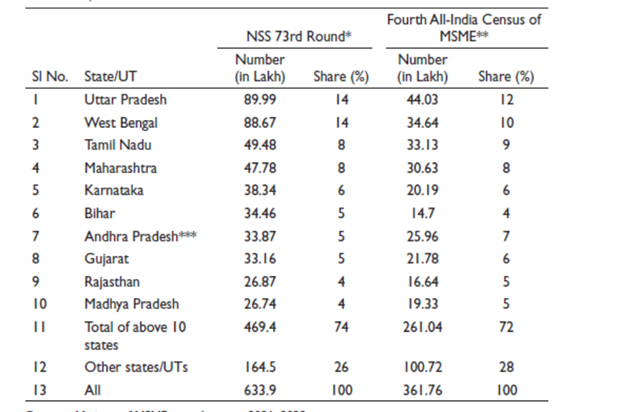 The National Sample Survey for Small and Medium Enterprises (NSS 73rd cycle) projects that 14.0 % of India’s MSMEs will be located in Uttar Pradesh. This is lists of the top 10 states in terms of the number of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), each of which is responsible for 74.00% of all MSMEs in the nation.
The National Sample Survey for Small and Medium Enterprises (NSS 73rd cycle) projects that 14.0 % of India’s MSMEs will be located in Uttar Pradesh. This is lists of the top 10 states in terms of the number of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), each of which is responsible for 74.00% of all MSMEs in the nation.
-
Diversity in Entrepreneurship
Businesses owned by micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) come from a wide variety of socioeconomic backgrounds. People from the upper class often run the show when it comes to big-time industries.
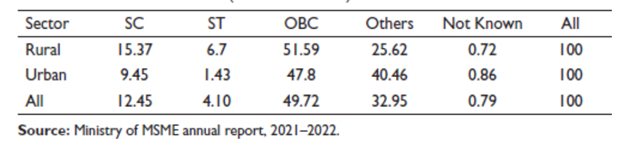 Business owners from OBCs accounted for 49.72% of MSMEs owned by socially disadvantaged groups, while SCs owned 12.45% and STs 4.10%, according to statistics from the 73rd round of the National Survey of Small and Medium Enterprises (NSS). Minority groups held nearly 73.67 percent of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) in rural areas.
Business owners from OBCs accounted for 49.72% of MSMEs owned by socially disadvantaged groups, while SCs owned 12.45% and STs 4.10%, according to statistics from the 73rd round of the National Survey of Small and Medium Enterprises (NSS). Minority groups held nearly 73.67 percent of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) in rural areas.
Participation of Women in MSMEs
There has been a gradual but steady shift in our traditional villages over the last many decades, and an increasing number of Indian women are entering the job.
 There may be more men than women in corporate America, but the number of women actively participating is on the rise.
There may be more men than women in corporate America, but the number of women actively participating is on the rise.
The MSME sector has opened doors for them to become entrepreneurs and boost the economy. As to the NSS 73rd cycle, the proportion of women-owned firms among all micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSME) in India was 20.37%.
MSME challenges in India
Despite the vital importance of the MSME sector to the Indian economy and inclusive growth in particular, the sector faces numerous challenges. The MSME challenges in India that are limiting the development as follows:
- The lack of sufficient and timely funding from banks was a challenge for the MSMEs. Now, micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) are not getting enough loans from banks. They frequently lack the capital necessary to purchase necessary machinery, equipment, and raw materials, sometimes even to cover their basic living costs.
- Multinational corporations and other huge businesses provide stiff competition for MSMEs as well. Companies with a global presence are providing reasonably priced, high-quality items.
- Infrastructural amenities are becoming scarce due to the increasing rise of MSMEs. They have a low manufacturing capacity and high production costs because to their inadequate infrastructure.
- Making things at affordable prices is challenging since there aren’t enough inputs like raw materials and trained workers on the market. Inadequate management skills, marketing channels, and brand development capacity are outcomes of the scarcity of skilled human resources among MSMEs, which is, in turn, caused by their low-paying capacity.
Lack of awareness of innovative industrial technologies is a consequence of both outdated technology and environmental constraints. They are still making things in the traditional manner.
- Accessibility to markets is a problem on a global and national scale. They have little resources for advertising and market research, making it difficult for them to sell their produce at competitive prices.
The MSME sector has shown remarkable innovation, adaptability, and resilience in the face of the many challenges it has faced.
Consequences for Policy
The Indian economy has grown at a remarkable pace during the past few years.
Slow poverty reduction, few high-quality job opportunities, widening provincial disparities, and increased inequalities between individuals and social groups are all signs that this growth has not improved the socioeconomic status of the population as a whole. The government has prioritized an inclusive growth approach in its government policies for MSME and thus sets the scenario for its necessity.
Because of their outsized impact on employment, exports, manufacturing output, GDP growth overall, and inclusive growth specifically, MSMEs, coupled with technology adoption in Indian MSMEs, play a significant part in the country’s overall development.
The MSME sector is currently contributing to inclusive growth in India by creating numerous job opportunities, reducing regional inequities, and bringing economically disadvantaged people into the mainstream.
Government initiatives like “Make in India” and “Digital India” present promising future prospects for the MSME sector.
However, the sector is about to grow because of a dearth of infrastructure, financial resources, and technological progress. The government may help the MSME sector overcome these challenges by increasing its support for it. It is necessary to take good care of this sector if we want this growth process to be inclusive.
Sustainable practices for small enterprises
The adoption of Sustainable practices for small enterprises is of the highest priority in order to mitigate their ecological footprint and secure enduring prosperity. These practices consist of:
- By utilizing energy-efficient equipment, implementing intelligent heating and cooling systems, and optimizing lighting solutions, small businesses can reduce their energy consumption.
- Small businesses can lessen their environmental impact by implementing waste reduction strategies such as composting, recycling, and the use of eco-friendly packaging.
- Keeping to sustainable and ethically sourced materials and ingredients can contribute to the implementation of eco-friendly practices across the entire supply chain.
- Small businesses can protect water resources by repairing leaks, instituting water-efficient practices in their daily operations, and utilizing water-saving technologies.
- Promoting public transportation, carpooling, and cycling minimizes carbon emissions and encourages sustainable commuting.
- Community involvement involves promoting positive relationships and contributing to the realization of a sustainable future by actively participating in local environmental initiatives, engaging in volunteer work, and promoting sustainable development projects.
Prospects for MSMEs in the Future
It is believed that India’s economy will surpass all others by 2025, with a GDP of $5 trillion and an annual growth rate of 8.5%.
When it comes to the future of the economy, micro, small, and medium-sized firms are going to be pivotal. Full development of MSME is necessary to create inclusive growth.
Supporting the nation’s ongoing and predicted rapid expansion might be MSMEs, with both domestic and foreign firms participating in the ‘Make in India’ campaign.
These areas can contribute to indigenization efforts. The idea of “Make in India with zero defect and zero effect” gives micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) an excellent opportunity to grow while reducing their negative effects on the environment.
One other great chance for micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) to increase their impact in the IT sector is the “Digital India” revolution. There is hope that India’s MSME sector can boost the country’s GDP.
There are a lot of opportunities to generate employment in this sector. Many people in rural areas work for small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs).
Consequently, this will help eradicate disparities across regions. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in India can greatly enhance the quantity and quality of the country’s exports. Foreign investment in this sector could be a boon for India’s economy.
If a country aspires to construct a strong MSME sector like those in countries where MSMEs contribute 35%-60% of GDP, it must invest in world-class technology adoption in Indian MSMEs and train its human resources. Governments should provide more support to MSME sectors if they want to foster an environment where these enterprises can prosper.
Financial Challenges
Finance and its accessibility pose a significant obstacle for MSMEs. In order to stay in business, this industry must overcome the financial struggles of small businesses.
1) Liquidity Crisis
Having access to the finances needed to operate day-to-day operations is a must for all businesses. Revenue from debtors is the principal source of readily available capital. If there is a shortfall in the funds from sales and accounts receivable, you can access short-term funding through bank overdrafts or cash credits.
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated MSMEs’ financial crisis. The bulk of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) rely on the success and credit payments from large corporations since they are suppliers to these firms.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) face liquidity problems when big corporations experience payment delays or operations shutdowns, which restrict the cash inflow to SME.
Bad debt or late repayment from creditors is a common issue for MSMEs since they lack appropriate recovery procedures, which impacts their working capital availability.
2) Access to Credit
The availability of credit is a key factor in both the expansion and diversion of a corporation, and it also plays a role in solving the liquidity crisis. One of the financial struggles of small businesses is the lack of access to sufficient and timely financing. The small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) sector has faced significant growth constraints due to the absence of sufficient and timely access to financing.
The MSME sector needs help from financial institutions in order to lower operating costs; however, not all financial institutions are accommodating when lending to this sector. The availability of credit becomes an issue as a result of this. Borrowing money from MSME comes with paperwork, long repayment terms, high-interest rates, and the need to put up collateral.
Due to the modest loan amounts, increased servicing costs, and limited ability of MSMEs to offer security against necessary financing, financial institutions have reduced their exposure to MSMEs.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) make up a sizable portion of the economy, yet banks are wary of providing loans to them. This has hampered the ability of MSMEs to take out loans, which has ruined their hopes of becoming financially independent.
3) Inadequate Financial Management
The success of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) is strongly correlated with their level of record-keeping and financial management. The company can reach new heights of success under the guidance of an owner or management who is financially savvy.
Available funds, allocation of funds, and evaluation of financial performance are all parts of financial management. If they have strong financial knowledge, they can craft a compelling proposition to issue the cash to the company.
One poor choice can drive up a company’s expenses. Therefore, it’s important for entrepreneurs to have a solid understanding of financial concepts. Increases in operational expenses could result from poor record-keeping. When operational costs are high, production costs are also high, which affects the bottom line of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs).
Borrowing money from banks is a challenge for many micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) since their employees lack expertise in managing money wisely and keeping accurate records.
Managing and securing funding is a big challenge for micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), as mentioned earlier. The Indian government is attempting to bolster the industry by flooding it with cash.
To solve the financial struggles of small businesses due to limited access to loans, the Ministry of Finance has implemented a number of programs. When business owners are resolute, these obstacles can be overcome with the help of government policies for MSME and financial institutions, ensuring the continued success of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSME).
Wrapping It Up
There would be no inclusive development, job creation, or economic growth in India without micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs). To overcome these challenges and guarantee the sector’s continued expansion, the government must implement regulations that support MSMEs, in addition to initiatives that encourage the adoption of technology and sustainable practices. MSMEs can succeed in today’s competitive business market if governments, banks, and entrepreneurs work together.
FAQs:
-
What are MSMEs?
The term “MSMEs” refers to micro-, small, and medium-sized enterprises that are extremely important to the growth of the international economy.
-
Could you tell me the number of MSMEs in India?
In India, more than six crore MSMEs are now in business.
-
How much of India’s exports are made up of MSMEs?
Small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) are responsible for around 50 % of India’s overall exports.
-
What hurdles do Indian MSMEs face?
Obstacles include limited access to finance, competition from larger corporations, infrastructure deficiencies, and technological constraints.
-
How does the financial crisis affect MSMEs?
Many micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) struggle to grow and remain in business because they lack the capital necessary to invest in necessary equipment, raw materials, and operating expenses.
-
How do Indian governments help MSMEs?
The goal of government programs like “Make in India” and “Digital India” is to help MSMEs grow by making it easier for them to do business and by promoting the use of new technologies.
-
Why should MSMEs adopt technology?
By increasing their competitiveness, efficiency, and productivity through the use of technology, MSMEs are able to expand their operations and tap into new markets.
-
How can MSMEs be sustainable?
Efficient use of energy, less waste, sustainable sourcing, conservation of water, environmentally friendly transportation, and involvement in the community are all examples of sustainable practices.
-
How do MSMEs contribute to inclusive growth?
MSMEs boost women’s economic independence, empower themselves, and lessen geographical inequities.
-
What role does the government play in MSME issues?
To aid MSMEs in overcome challenges and achieving long-term success, government initiatives offer financial aid, support for capacity-building, and access to markets.
