An Income Tax Return (ITR) is a document that a taxpayer uses to disclose his income, costs, tax deductions, purchases, and taxes. The Income-tax Act of 1961 requires taxpayers to file an income tax return under various scenarios.
However, there may be additional reasons to file an income tax return even if you do not have the required income, such as carrying forward losses, claiming an income tax refund, applying for a VISA, a loan from a bank, term insurance, and so on.
E-filing is the process of filing an Income Tax Return (ITR) online using the Internet. Individuals can use PAN-based login credentials to access the new income tax portal, which has various features that make the tax filing process more accessible.
What is an ITR filing?
Income Tax Returns, or ITR filing, is filling out an income tax* form that allows you to declare the taxes you paid in the current year based on your income tax slab. There are seven different ITR forms: ITR 1, ITR 2, ITR 3, ITR 4, ITR 5, ITR 6, and ITR 7.
This form, which must be completed by the appropriate type of taxpayer, reports income, expenses, and other vital tax* information to the tax authorities. Taxpayers should determine which sort of ITR form they need to fill out before completing their returns, and the forms depend on their income.
ITR Filing for Salaried Individuals
To file ITR as a salaried individual or professional income, you must have access to a computer and download the ITR-1 Sahaj. Here’s how to proceed:
- Visit the Income Tax Department’s official website: https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal.
- You can access your account using your PAN card, password, and a captcha code.
- Go through the “e-File” menu and select “Income Tax Return”.
- After clicking the “Income Tax Return” link, you can view your PAN. Select the assessment year, ITR form number, and filing type “Original/Revised Return.”
- Select “Prepare and Submit Online” mode and complete the ITR form.
- Select a verification method and click the “Preview and Submit Button.”
- You can now open and view the uploaded file.
ITR Filing for Business and Professions
Every corporation, regardless of its commercial activity throughout a fiscal year, must file income tax* returns, even if it has incurred losses. Partnership firms submit a NIL income tax* return by the due date.
However, this is not the case for self-employed professional income; if they have no operations to show during the fiscal year, self-employed professionals are not required to file income tax* returns using the self-employed ITR form for that fiscal year.
Filing income tax* returns for a business, a firm, or the self-employed requires access to a computer to download the form ITR-4 Sugam. Follow the steps below:
Proprietorship Tax Rate (AY 2024-25| FY 2023-24) under Normal Tax Regime
Proprietorship Tax Rate AY 2023-24| FY 2022-23—The proprietor’s age is less than 60.
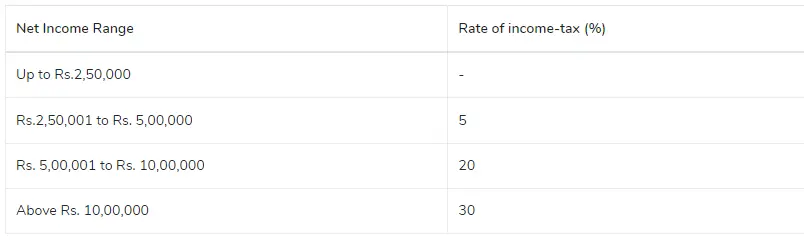
Proprietorship Tax Rate AY 2023-24| FY 2022-23-The Proprietor’s age ranges from 60 to 80 years
The following tax rate applies to a Proprietor who turns 60 during the preceding year but is under 80 on the last day of the previous year.
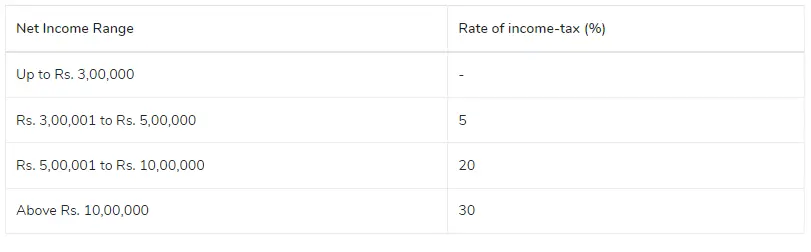
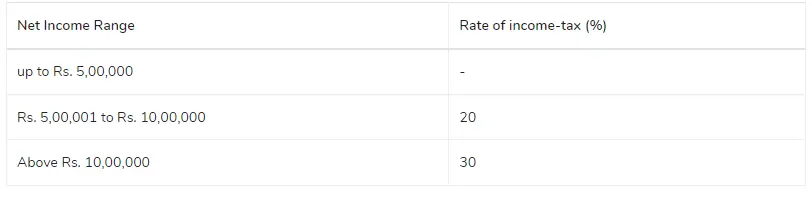
Proprietorship Tax Rate AY 2023-24 | FY 2022-23-Proprietor’s Age is Over 80 Years
Online ITR for Business Income
Only the ITR-4 can be filed online, and you must comprehend the following steps. When filling out the form online, you must supply the information directly on the form before submitting it. Individuals and self-employed persons can use this ITR form to file their taxes.
- For ITR-4 filing, visit the official income tax* e-filing website at https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal.
- You can access your account by entering your PAN, password, and captcha code.
- Under the “e-file” menu, choose “Income Tax Return.”
- The page will fill up your PAN information. You must give the assessment year, the ITR form number, the filing type “Original/Revised Return,” and the submission mode “Prepare and Submit Online.”
- Click “Continue.”
- Follow the instructions and then fill out the ITR-4 form. To preserve the details, press the “Save Draft” button regularly.
- Once this step is done, select your preferred verification option.
- Choose the “Preview and Submit” option.
- Recheck and verify all of the information you have supplied.
- Submit the ITR form.
- Once your tax* returns have been confirmed online, you can access your ITR file through your account.
What documentation is required by a businessman or professional when filing an ITR?
If you select for the presumed scheme as a businessman under section 44AD or as a professional under section 44ADA, you just need the following information:
- Gross Turnover / Receipts
- Gross profit
- Other information includes Sundry Debtors, Sundry Creditors, Stock in Trade, and the cash balance at the end of the year.
- It is also necessary to reconcile your 26AS statement to ensure that the TDS deducted in your business name is totally and correctly reported.
Suppose you are conducting a business (without opting for presumptive taxation) and your total turnover or sales reach Rs. 1 crore during the fiscal year. In that case, you must have your accounts audited under section 44AB. This ceiling of 10 crores will apply beginning with the fiscal year 2021-22.
Also, a professional with a total receipt of more than Rs 50 lakhs, such as chartered accountants, doctors, or lawyers, must have their accounts audited. In the event of an audit, all accounts must be properly preserved.
Also Read: Last Date for Filing Income Tax Returns in India 2024
Practical Tips For the New Financial Year
Determine your taxable income precisely.
Make sure you don’t neglect any other sources of income besides your wage or company revenue, such as interest from savings accounts and fixed deposits, capital gains, dividend income, rental income, income from foreign assets, and so on.
Remember to declare any capital losses from investments since they can be used to offset other gains and reduce taxable income.
Unadjusted losses can be carried forward up to eight financial years. Calculate your capital gains or losses using the statement issued by your stockbroker or mutual fund.
Report all of your claims and deductions appropriately.
Claim all eligible deductions under the Income Tax Act, including Sections 80C, 80D, and 80G, to decrease your tax payment. Don’t miss out on exemptions such as savings bank interest up to Rs 10,000 and deductible expenses like early medical check-ups up to Rs 5000.
Verify Form 26AS and the Annual Information Statement (AIS).
These documents are necessary for tax filing. You can access these papers through the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal. Form 26AS, often known as a tax passbook, provides information on TDS, TCS, high-value investments, and property purchases.
The Annual Information Statement (AIS) is an extension of Form 26AS that covers interest, dividends, securities/mutual fund transactions, and international remittance information.
To avoid rejection by the IT department, ensure that all details in these documents match those on your Form 16, bank account statements, and financial records.
Select the appropriate ITR form.
The IT department has developed many income tax return forms, including ITRs 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. The relevant form is determined by your income source, earnings, and taxpayer category.
ITR 1 is appropriate for those earning up to Rs. 50 lakh from salaries, one residential property, other sources (e.g., interest), and agricultural income up to Rs. 5,000.
ITR 2 applies to individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) who do not earn revenues from their company or profession. TR 3 applies to people and HUFs who earn money from their business or profession.
Gather all the essential documentation.
Keep accurate records of all papers, including PAN, Aadhaar, Form 16, Form 26AS, AIS, TDS certificates, advance tax payment receipts, investment evidence, etc. Keep these documents accessible to avoid last-minute issues during ITR filing.
Ensure your bank account information is correct.
To receive your tax refund on schedule, double-check and authenticate your bank account data. Any errors in the bank data will cause reimbursements to be delayed.
Remember to verify your ITR to complete the filing process.
After submitting your returns, remember to complete the filing process by certifying your ITR within 30 days. To verify, use Aadhaar OTP online or send a signed ITR-V form to the IT department’s central processing center in Bengaluru.
What are the necessary documents for filing an ITR?
Income Tax Return (ITR) paperwork differs depending on the tax filer’s source of income. However, specific documentation is required for all taxpayers, regardless of income source. Here is a list of such standard ITR documents that are necessary to file an ITR in FY 2022-23 (AY 2023-24).
PAN Card
A PAN Card is mandatory for submitting income tax returns. PAN is also essential to deduct TDS and should be linked to your bank account for direct credit of your income tax refund (if applicable).
It is issued by the Income Tax Department, and a salaried employee can obtain it from a PAN card, Form 26AS, Form 16, Form 12BB, etc.
However, after a recent government reform, taxpayers can now file the ITR using their Aadhaar number rather than their PAN number.
Aadhaar card
Section 139AA of the Income Tax Act requires individuals to furnish their Aadhaar card information when filing returns.
If you don’t have an Aadhaar card but have applied for one, you must provide the enrolment ID in your IT returns. Linking your PAN and Aadhar enables you to validate your income tax return online using an OTP.
UIDAI issues Aadhar cards. If you have misplaced or cannot find your Aadhaar card, you can download it online.
Form 16
This form contains information on the employee’s salary and the amount of TDS taken from it. Form 16 has two parts: Part A and Part B.
Part A contains information about how much tax the employer deducted throughout the fiscal year, as well as the employer’s PAN and TAN.
Part B of the form includes TDS computations such as gross pay breakdown, exempt allowances, and perquisites.
Please take note that Form 16 is issued by the employer. It is an essential document for a salaried individual filing an ITR.
Form-16A/16B/16C
Form-16A is utilized for reporting TDS collected on payments besides wages, such as earnings from recurring deposits, fixed deposits, and so on. If a person sells their property, Form-16B is issued.
It includes information regarding TDS deducted from the amount paid to the vendor. Form 16C is a TDS certificate that shows the TDS deducted on rent at 5% by an individual or HUF under Section 194IB.
Form 16A is issued by deductors, such as banks and contractors. In contrast, Form 16B is issued by the buyer. Also, a person collecting TDS on rent must deliver Form 16C to the payee 15 days after filing the Challan cum statement in Form 26QC. The TDS details can also be obtained from your Form 26AS.
Bank Account Details
Disclosure of all active bank accounts is required in the ITR. Bank account information such as your bank name, account number, IFSC, and the number of accounts you own must be included in your income tax return.
Also, one account will be designated as primary to aid the Income Tax Department in refunding your tax refund via electronic transfer to that account.
Bank information is utilized to verify your income reports, large-volume transactions, and so forth. These facts are easily obtained in bank passbooks, checkbooks, statements, net banking accounts, and so on.
Bank Statement/Passbook
Bank statements offer the details of the interest generated on a savings account, interest income on fixed deposits, and so on during a fiscal year. These details are essential while filing an ITR.
Form 26AS with AIS/TIS
It is an annual tax statement, similar to a tax passbook, that includes information on all taxes deposited against your PAN. This includes:
TDS may be deducted from your payments by the bank, employer, or other entities.
The individual should ensure that all taxes deducted throughout the fiscal year are reported against the PAN on Form-26AS. In the event of a mismatch, you will be unable to claim the tax credit for the TDS deduction. As a result, the issue should be resolved by contacting the deductor.
Signing into your account on the Income Tax India e-filing website will allow you to view Form 26AS for the applicable Assessment Year.
AIS: The Annual Information Statement (AIS) provides a comprehensive perspective of a taxpayer’s data as reported on Form 26AS. Taxpayers can comment on the information displayed in AIS. Under each part (TDS, SFT, Other information), AIS displays both the reported value and the updated value (the value after taking into account taxpayer feedback).
TIS: Taxpayer Information Summary (TIS) is an aggregated summary of a taxpayer’s information by category. It displays the processed value (i.e., the value generated after deduplication of information using predefined rules) and derived value (i.e., the value derived after incorporating taxpayer feedback and processed value) for each information category (e.g., salary, interest, dividend, etc.). The extracted data contained in TIS will be utilized to prefill the return, if applicable.
Home Loan Statement
Individuals receive loan statements that include information such as principal and interest payments. This breakdown information is required as verification and information when filing your income tax returns.
If the client has taken out a home loan from a financial institution such as a bank, he or she should obtain the statement for the previous fiscal year.
Tax-saving instruments
If you have invested in any tax-saving schemes, such as tax-saving FDs, ELSS, or investment receipts, you should have the necessary papers when filing your taxes.
Capital Gains Details
If you sell shares, stocks, or property, you will incur a capital gain or loss. You will require documentation such as broker statements, property sales deeds, and so on.
Rental Income
If you earn money from your house or property, you must record it while completing your income tax return. Also, if you are paying rent, remember to get receipts from the landlord.
These documents, however, are not required to be submitted with the ITR, but they should be kept safe in case they are needed later by your employer or the income tax department.
Foreign Income
Documents for any income made in or from a foreign nation during a job deployment or for a portion of the year should be sent to your tax expert in order to claim tax credits and DTAA. Any papers for overseas revenue must be arranged with the employer or contractor.
Dividend Income
If you invested in stocks or mutual funds and received dividend income, you should disclose it on your tax return.
Dividends earned during the fiscal year can be obtained from your broker statement or Demat account summary.
Why is it essential to file your income tax return?
Individuals must file returns only if their income exceeds the basic exemption limit or if they meet specific criteria, such as spending more than Rs.2 lakh on foreign travel, consuming Rs.1 lakh or more on electricity, and depositing an amount/aggregate of more than Rs.1 crore in one or more current accounts in FY 2019-20 or later.
ITR filing is also necessary if company revenues surpass Rs.60 lakhs, professional payments exceed Rs.10 lakhs, or TDS and TCS totals exceed Rs.25,000.
If you are a resident with an asset outside of India or have signing power for an account-based account outside of India, it is always a good idea to file your ITR, even if you are not qualified for the advantages.
- Filing an ITR provides documentation of income and net worth, which is essential for future loans and credit card applications.
- ITRs are necessary for visa applications and other purposes.
- ITR is essential to receive term insurance.
- ITRs are necessary for getting government tenders.
As a result, it is recommended that you submit an ITR even if your income is less than the basic exemption amount.
Latest Update on ITR Return Filing
The Noble Bombay High Court has asked the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) to immediately publish a notification extending the deadline for filing updated and belated ITRs to January 15, 2025. This deadline has been extended for taxpayers who are entitled to claim the section 87A tax rebate. Please keep in mind that this is simply an interim remedy; the ultimate judgment will be handed down on January 9, 2025.
What did the Bombay High Court do?
The Bombay High Court issued an order on December 20, 2024, directing the Central Board of Direct Taxes to extend the deadline for e-filing income-tax returns from December 31, 2024 to January 15, 2025. This extension is intended to guarantee that all taxpayers qualifying for the rebate under Section 87A have the chance to exercise their statutory entitlements without encountering administrative barriers.”
What is the Section 87A tax rebate issue?
According to Anand Bathiya, president of the Bombay Chartered Accountants’ Society (BCAS), “Post 5th July 2024, the income tax return (ITR) filing utilities are not allowing the rebate under section 87A for various special rate incomes, including short-term capital gains on equity shares or equity oriented mutual funds taxable at 15% under Section 111A.”
According to the Bombay High Court ruling, the Chamber of Tax Consultants stated that “the respondents have unilaterally disabled assesses from claiming rebate under Section 87A after 5 July 2024 by modifying the utility software for filing income-tax returns.” As a result, if assesses file their returns using responders’ software after July 5, 2024, they will be unable to claim the rebate.
The Finance Act of 2019 raised the threshold for receiving a tax rebate under section 87A to Rs 12,500 if income was Rs 5 lakh or less under the previous tax regime. According to the new tax regime, the tax rebate amount is Rs 25,000 if the income is Rs 7 lakh or less.
“The principle behind Section 87A has always been to ensure that taxpayers in lower-income brackets are not burdened unduly, and the arbitrary disabling of the rebate through the modification of utility software undermines this legislative intent,” reported The Chamber of Tax Consultants.
Sweta Upadhyay, Senior Associate, “subject to the notification to be issued u/s 119 of the Act, the taxpayers are eligible to claim rebate u/s 87A of the Act by filing a revised return up to 15th January 2025, as procedural changes, such as those in utility software or instructions issued by the tax department, cannot override substantive right to rebate.”
Wrapping It Up
When filing tax* returns as a company, proprietorship, salaried, or self-employed individual, all you need is the correct information on the appropriate ITR forms to assist you with your returns. While the process may take some time and patience, filing your tax returns online has made it much more manageable. To guarantee that you complete the procedure in one sitting, make sure you have all of your documentation ready before you begin completing your returns.
Also Read: What Are The Benefits Of Integrating GST Registration With Your Invoice/ Billing Software?
Also Listen: GSTN: Know Complete Lists of Central Govt approved Accounting and Billing Software
FAQs
-
Which ITR form is for self-employed individuals?
Self-employed people can file their income tax returns using the ITR-4 or ITR-4S forms.
-
How much money is tax-free?
Income ranging from 0 to Rs 3 lakh is tax-free under the new regime. As a result, this income will be tax-free.
-
Do we need to show proof of 80C when submitting the ITR?
You are not required to produce any papers to the tax department in order to claim these deductions when completing your tax returns.
-
What does “TDS” represent in terms of income tax?
TDS stands for Tax Deducted at Source. Under this method, if a person (deductor) is required to pay another person (deductee), the deductor will deduct tax at the source and transmit the balance to the deductee. The TDS amount deducted will be sent to the central government.
-
Who collects the TDS?
The employer collects funds from the taxpayer and deposits them with the IT Department on their behalf.
-
What is the complete form of the ITR?
Income Tax Return (ITR) is a form that a person must submit to the Income Tax Department of India.
-
What happens if the income tax refund is more than $50,000?
If your refund exceeds Rs 50,000, the Income Tax Department may conduct additional checks.
-
Is a salary of Rs. 10 lakhs tax-free?
If you choose taxes-saving options and claim all relevant deductions and exemptions, you can pay no income tax on a ten lakh wage.
-
Can I claim LTA in my ITR filing?
The LTA exemption amount, which can be claimed as a tax-free expense, is determined by the actual cost of travel.
-
How many different types of returns are there in the ITR?
How many ITR forms are accessible to individuals? Individuals can submit seven ITR forms: ITR 1, ITR 2, ITR 3, ITR 4, ITR 5, ITR 6, and ITR 7.
