The introduction of GST is a significant step in indirect tax reform in India. The elimination of the cascading effect of taxes has made our products competitive in the domestic and international markets, leading to greater economic growth in the country. It has widened the tax base, increased trade volumes, and brought transparency and efficiency to the indirect tax system. Most importantly, the online-based procedures have made administration easier for the tax authorities and compliance simpler for the taxpayers.
As compliance laws become stricter with regular amendments and advisories passed by the GST council, it is important for taxpayers to ensure correct reporting and accurate filing of returns. Downloading the GST summary is crucial for businesses, as they can reconcile the data and modify it wherever necessary before filing the periodic mandatory returns. Once the returns are filed, modifications or deletions are not allowed. The changes must be incorporated into the next return.
What is a GST return?
A document containing details of all sales and purchases, tax collected, tax paid, and input tax credit availed must be furnished by registered taxpayers on the GST portal provided by the government. This document is called the GST return.
All taxpayers registered under GST are required to file their GST returns according to the nature of their business. The types of businesses that are required to file returns are:
- Regular businesses
- Businesses registered under the composition scheme
- Other types of businesses
- Auto-drafted returns
- Amendments
- Tax notices.
Types of GST returns
1. Regular businesses
The important returns that a regular taxpayer has to file are as follows:
GSTR-1: Gstr-1 is a return consisting of all outward supplies made, including interstate, intrastate, B2B, and B2C purchases made under reverse charge and interstate stock transfers made during the tax period.
GSTR-3B: This return is a consolidated summary return of inward and outward supplies, tax liabilities, and ITC claims. The purpose of the return is for the taxpayers to declare the summary of their GST liabilities for a particular tax period and discharge the liabilities.
GSTR-9: This is a consolidated annual return containing the details of purchases, sales, input tax credit, refund, demand created, etc. It is a consolidation of the monthly and quarterly GST returns of the taxpayer. In other words, the return is a compilation of all business transactions in a particular financial year.
GSTR-9C: This is an audit form for taxpayers whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds Rs 5 crore. It is a self-certified reconciliation statement that taxpayers must submit along with the audited annual accounts of their business.
2. Businesses registered under the composition scheme
The important returns that businesses registered under the composition scheme need to furnish are as follows:
GSTR-4: GSTR-4 is an annual return that taxpayers registered under the composition scheme need to file. It consists of the total value of outward supplies, inward supplies, and imports of services and supplies attracting a reverse charge of the business for the specific period.
GSTR-9A: This is an annual return that must be filed by taxpayers who have opted for the composition scheme every financial year. It consists of details of outward supplies, inward supplies, taxes paid, refund claimed, input tax credit availed or reversed.
3. Other types of Businesses
- GSTR-5: Non-resident foreign taxpayers must file this return. It consists of details of the taxpayer and invoice details of all goods and services supplied and purchased, including imports into India by the taxpayer during the registered period.
- GSTR-6: This is a monthly return that input service distributors (ISDs) must file. It contains invoice-level supply details from GSTR-1 of counterparties, credit details of ITC received, and details of ITC reversed or distributed during the period to which the return pertains.
- GSTR-7: This is a monthly return that taxpayers who deduct tax at source must file. It consists of details of invoices and the tax deducted, with bifurcation under SGST, CGST, and IGST. It also includes details like interest and penalties.
- GSTR-8: This is a monthly return for e-commerce operators consisting of details of supplies made to customers through the e-commerce portal by both registered and unregistered taxpayers, the amount of tax collected at source, tax payable and tax paid.
- GSTR-9B: This is an annual return that e-commerce operators who collect tax at source must file. It is a summary of outward supplies of goods and services, the amount of tax collected, purchases made, and basic information about the taxpayer.
- GSTR-10: This is the final return that must be filed when a business ends its business permanently and cancels its GST registration. It contains the details of all supplies, liabilities, tax collected, tax payable, etc.
- GSTR-11: It is a statement of the inward supply of goods or services, or both, received by UIN holders. They must file this statement on a quarterly basis.
4. Auto-drafted returns
- GSTR-2A: This return is auto-populated with details of inward supplies made by a taxpayer that are auto-populated based on the details updated by the supplier in his GSTR-1.
- GSTR-2B: This is an auto-drafted input tax credit statement. It is generated for every normal taxpayer based on the information provided by the taxpayer’s suppliers in their respective GSTR-1, IFFs, GSTR-5 (Non-resident taxpayers) and GSTR-6 (input service distributors)
- GSTR-4A: This is an auto-drafted and view-only form for composition taxpayers. It is created on the basis of the data furnished by the suppliers in their GSTR-1 and 5, in which the taxpayers are the recipients.
5. Tax Notice
- GSTR-3A: This is a system-generated notice that is issued to taxpayers who have not filed the returns in Form GSTR-3B or any other return within the due date.
Filing GST returns
All businesses registered under GST are required to file returns like GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, GSTR-4, GSTR-9, and GSTR-9C, based on the type of business and category of registration. Accurate and timely filing of returns is crucial to staying compliant and avoiding penalties and other legal consequences.
Track and view filed returns
GSTN has provided an option for taxpayers to track their return status and download the filed returns. The steps are as follows:
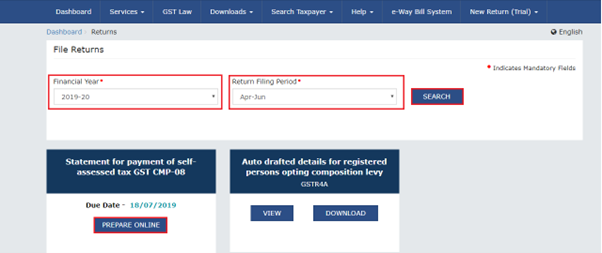
Step 1
Access the home page of the GST portal at https://www.gst.gov.in/
Login with valid credentials, click on services>returns>view filed returns option
Step 2
Select the relevant return filing period and return type from the drop-down list
Step 3
Click on the search option, and the search results are displayed.
Step 4
Click on view link to view the filed return.
Step 5
To download the signed form, click on the download link. It takes 5 minutes for the form to be generated.
Also Read: How do I get a GST Summary?
Step-by-step guide to download the GST summary
The taxpayer must perform the following steps to view and download the GST summary:
Step 1: Login to GST portal
- The taxpayer must access the portal at https://www.gst.gov.in/. The GST homepage is displayed.
- The taxpayer must login with his valid credentials, like username and password.
Step 2: Navigate to returns dashboard and select the appropriate period
- Navigate to the services>returns>view filed returns option.
- Select the financial year, return filing period, and return type from the drop-down list.
- Select the required GST return from the drop-down menu. Scroll down to the bottom of the GST return form.
Step 3: Click on ‘generate GST summary’
The invoices added by the taxpayer will get reflected in the relevant section of the GST return form. The summary can be seen instantly after adding the invoices. The summary gets generated automatically at an interval of 30 minutes.
The taxpayer can also check if any error files are generated during the upload of the JSON file in the offline method. They can download the error file and make the required corrections.
After clicking the search button, for normal taxpayers, GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B will be listed and for composition taxpayers, CMP-08, GSTR-4, GSTR-4 (Annual) will be listed.
- Select GSTR-1 from the drop-down list
- The taxpayer can view the filed returns.
- To download the signed form, click on the generate summary link
Step 4-Download the summary
Click on the download summary option by selecting either pdf or excel format. Verify the downloaded summary for accuracy and save it for further use.
Conclusion
Downloading the summary is very important, as it can be used to check the accuracy of the details entered and make modifications wherever required. Because once the returns are filed, changes like additions or deletions of the details cannot be made. The summary contains the details of all the financial transactions pertaining to the business during the tax period and the tax payable on them. It helps in reconciling the GST data with the books of accounts of the taxpayers and fulfills the compliance requirements. Accurate and timely filing of the returns helps in ensuring that the credit flows to the right people. It provides transparency and accountability in the indirect taxation system in the country.
Frequently asked questions
How are the differences found in the GST summary rectified?
Answer: The differences found in the GST summary can be rectified by updating the date furnished. In auto populated returns, communication between taxpayers is necessary to rectify the differences in the invoice details uploaded in the portal. For this a facility is provided by GSTN on the portal.
What is the communication between taxpayers?
Answer: Communication between taxpayers’ functionality is provided by GSTN to facilitate the taxpayer’s ability to communicate with the counterparty and request an action on the document furnished or uploaded by him or by the counterparty through the GST portal.
Which types of taxpayers are eligible to use the communication between taxpayers functionality?
Answer: All registered taxpayers except those registered as taxpayers under TDS, TCS, and NRTP are able to access the link to the communication between taxpayers functionality.
