INTRODUCTION
E-waybills, or electronic waybills are essential to the efficient flow of goods. Regarding the duration of these documents’ validity, each state may have its own regulations.
This article will guide you through the process of extending the validity of an E-waybill by examining the specific standards set forth by each state.
Understanding these state-specific details is crucial for assuring compliance and hassle-free transportation, whether you’re a business owner or responsible for logistics.
Let’s explore the field of E-waybills and learn about the various regulations in the various states.
Variations in E-waybill extension requirements across states
The following typical variations in E-waybill extension requirements exist between states:
- Extension Periods: Certain states may permit extensions beyond the regular validity term that are either longer or shorter. It is essential to understand these differences.
- Reasons for Extension: States may decide to extend an E-waybill under certain guidelines or for specific purposes. These justifications could vary, ranging from unexpected occurrences to formalities.
- Documentation: A different set of documentation may be necessary in each state to support an extension of an E-waybill. This may involve offering more details or supporting data for the extension.
- Extension Process: Extending an E-waybill may include several procedural stages. While some states might offer an online application process, others can need paperwork or further approvals.
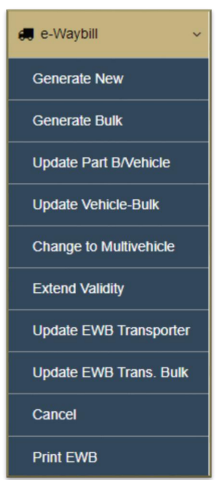
OPTIONS UNDER E-WAYBILL
- Applicability to Different Sectors: Depending on the type of goods or sectors, some states may have sector-specific differences in the requirements for E-waybill extensions.
- Communication Protocols: States may follow different procedures for informing the appropriate parties, like consignors, consignees, and transporters, of E-waybill extensions.
- Exceptional Circumstances: States can handle E-waybill extensions differently due to extraordinary situations such as transshipment, allowing for flexibility, or enforcing additional requirements.
- Frequency of Extensions: The frequency of E-waybill extensions within a certain period may be restricted by some states, which could affect how companies schedule their transportation needs.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: States can impose different penalties from fines to other repercussions for violating the E-waybill extension criteria.
- Integration with State-Specific Systems: The extent to which state-specific systems are integrated with E-waybill extension procedures varies, which can impact the accuracy and efficiency of the extension process.
Legal considerations for interstate E-waybill extension
To guarantee compliance with laws and prevent potential penalties, legal considerations for interstate E-waybill extensions are crucial. Important legal considerations are as follows:
- Recognize and abide by the state-specific E-waybill laws that apply to interstate movement. Regarding validity periods and extensions, different states may have different regulations.
- Verify that the justifications for the E-waybill extension meet the legitimate requirements outlined in the pertinent state regulations. Unexpected incidents, transshipments, and other extraordinary situations can all be acceptable explanations.
- Observe any deadlines set forth for informing the appropriate authorities of the extension. To prevent non-compliance problems, timely communication is often necessary.
- Keep thorough records of the E-waybill extension procedure. This includes documenting the dates, the justifications for the extensions, and any permissions received. Maintaining thorough records is essential for regulatory compliance and audits.
- Follow any special authorization guidelines provided by state laws. Extensions of E-waybills may require government acknowledgment or approval in several states.
- Make sure that the procedures for extending an E-waybill comply with the rules regarding the Goods and Services Tax (GST) that apply to interstate transportation. Adherence to the GST requirements is essential for legal compliance.
- Make sure that everyone who needs to know about the E-waybill extension receives notification, including the transporters, consignees, and consignors. For legal compliance, open communication is essential.
- Follow any revisions or modifications to the E-waybill laws in the relevant states with regular attention. Keeping up with legal changes guarantees constant compliance.
- Ascertain that the legal procedures for managing such exceptions are observed if the extension is the result of extraordinary events, such as transshipment. Additional paperwork and approvals might be essential for this.
Compliance obligations in meeting state-specific extension rules
Adhering to state-specific extension regulations for E-waybills necessitates strict compliance requirements. Companies who want to extend the validity of an E-waybill must be aware of and compliant with the state-specific regulations.
It includes notifying the relevant authorities as soon as possible, maintaining documentation of the extension procedure, and obtaining any required licenses or authorizations. Also, confirming that the justifications for the extension comply with the legal criteria outlined in state law.
Maintaining open communication channels with every individual participating in the transportation process, including carriers, consignees, and consignors is crucial. It helps businesses to ensure the seamless and lawful interstate transportation of goods and prevent potential penalties by routinely adhering to these compliance standards.
Documentation needed for complying with diverse state requirements
Extending an e-waybill requires extensive documentation. The following is a list of necessary documents to guarantee adherence:
- E-waybill: Keep a print of the original E-waybill information, including the consignment details, E-waybill number, and the duration of initial validity.
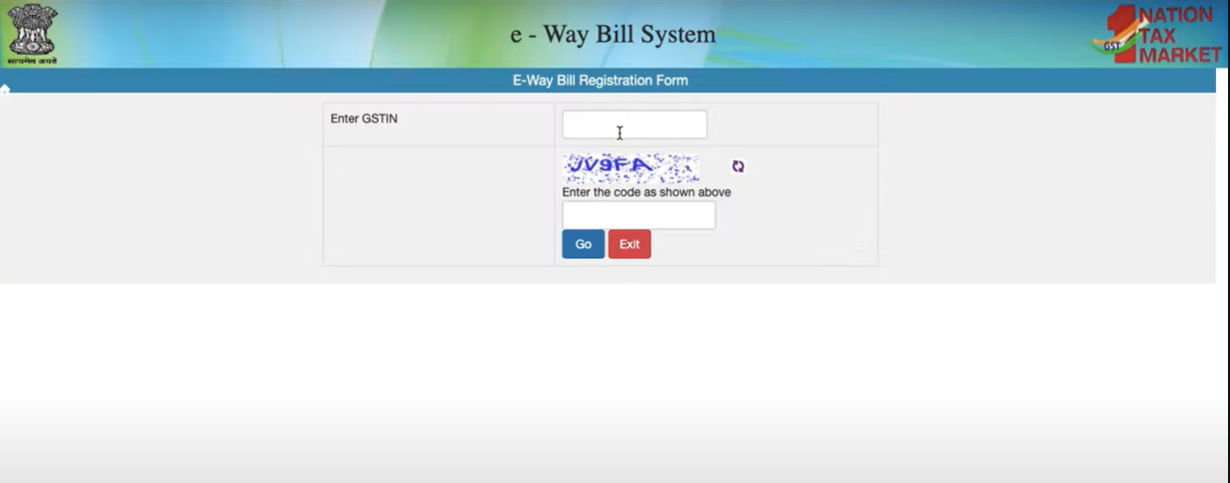
FORM 1 OF PRINT E-WAYBILL
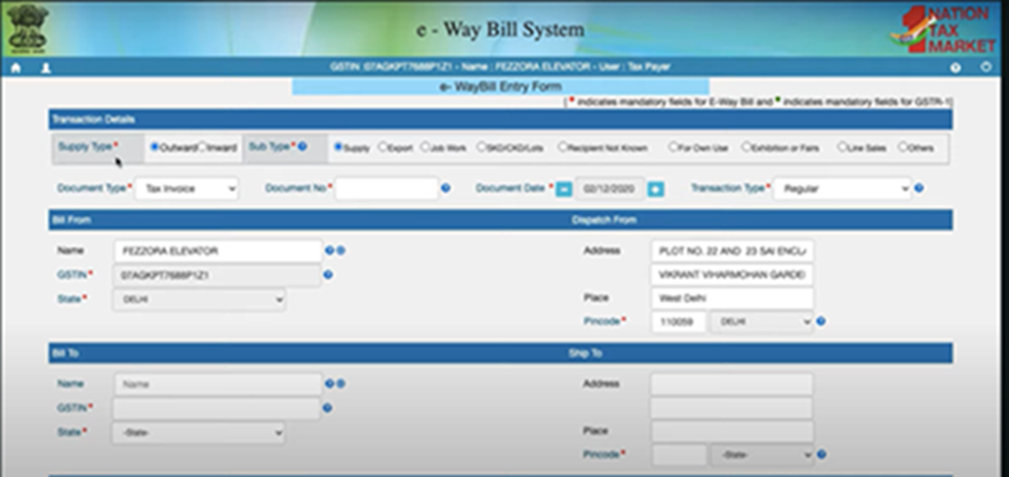
FORM 2 OF PRINT E-WAYBILL
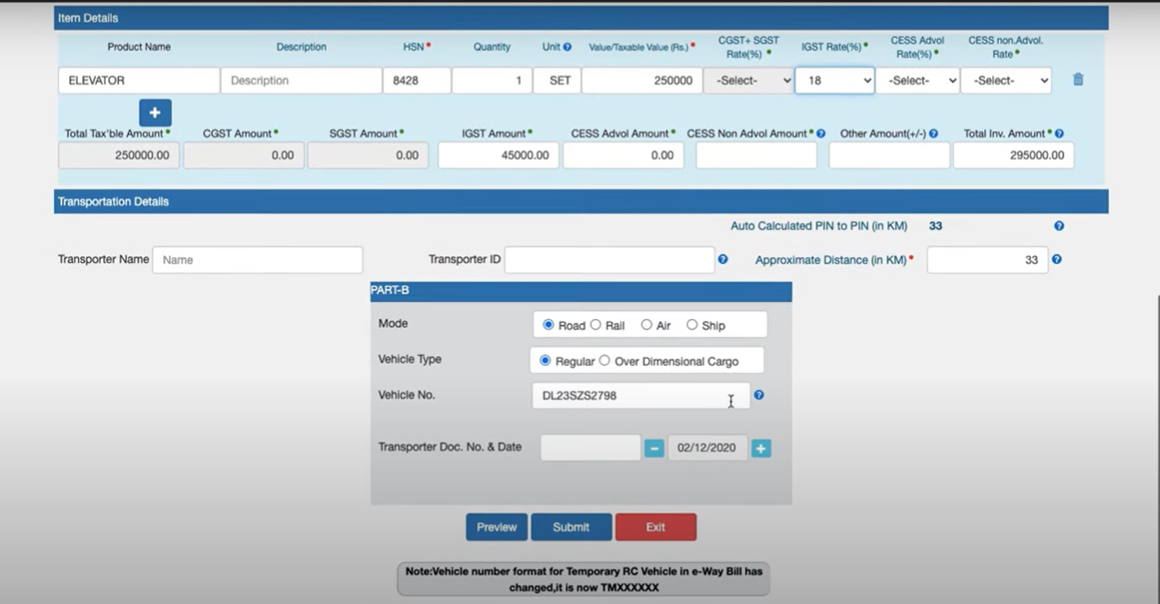
FORM 3 OF PRINT E-WAYBILL
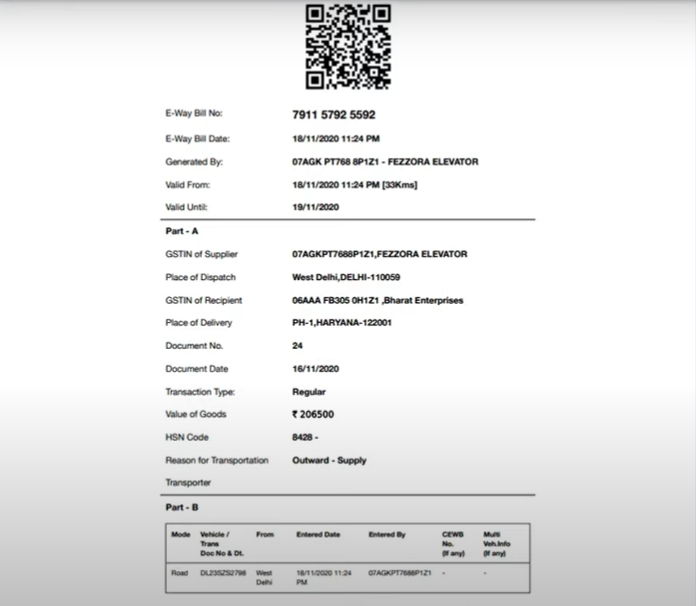
FINAL PRINT OF THE E-WAYBILL
- Cause of Extension: Specify the cause of the E-waybill extension, being careful to ensure that your explanation complies with state regulations.
- State-Specific Forms: Fill out and submit any state-specific applications or forms necessary to extend an E-waybill. There may be distinct documentation procedures in some states.
- Permission Approvals: Maintain records of any authorizations you receive from the appropriate authorities if state regulations need permission for E-waybill extensions.
- Records of Prompt Notifications: Preserve documentation of prompt notifications concerning the E-waybill extension that were transferred to the relevant state authorities. This contains information such as dates, channels of contact, and any acknowledgments that were made.
- Communication Records with Relevant Parties: Keep a record of every communication regarding the E-waybill extension that you have with all the relevant parties participating in the transportation process, including consignors, consignees, and transporters.
- Documentation for Exception Handling: If the delay results from extraordinary events (such as a transshipment), maintain supplementary records outlining the specifics of the situation and any authorizations that may have been granted.
- Record of State-Specific Regulations: Keep an extensive file detailing the E-waybill laws that apply in each of the participating states. This guarantees that documentation complies with each jurisdiction’s particular criteria.
- Audit Trail Documentation: Maintaining an audit trail that records all aspects of the E-waybill extension’s lifespan, from the beginning to the conclusion, is crucial. In the event of an audit, this trail acts as proof of compliance.
Also Read: Procedures and Documentation for Handling Expired E-waybills
Reporting obligations for extended E-waybills in different states
To ensure a seamless and legal flow of goods, it is essential to report extended E-waybills across different states. The regulations and specifications for E-waybills, including their validity periods, vary from state to state.
Businesses can contribute to clear and effective logistics operations in addition to adhering to these state-specific rules by reporting E-waybill extensions.
Prompt reporting ensures that the transportation process complies with the various regulatory requirements of each state by informing authorities of any changes. This promotes dependability and trust in interstate commerce in addition to aiding in avoiding fines for non-compliance.
Transmitting extended E-waybills is essentially a proactive measure that facilitates the smooth and lawful transportation of goods between many states by assisting with the intricacies of state-specific legislation.
Challenges in navigating state-wise E-waybill extension differences
Differentiations in e-waybill extensions cause several difficulties for companies that handle interstate transportation. The following are the main challenges:
| Diverse State Regulations |
|
| Changing Legal Landscape |
|
| Authorization Protocols |
|
| Communication Challenges |
|
| Record-Keeping Complexity |
|
| Operational Delays |
|
| Technology Integration Issues |
|
Also Read: Challenges and Solutions in Import E-waybill Compliance: Cross-border Considerations
Exemption considerations for specific interstate scenarios
Depending on state laws and unique circumstances, there may be different exemptions for different interstate E-waybill extensions. Typical exclusions might consist of:
- Force Majeure Events: In situations where unanticipated circumstances or natural disasters prevent the timely extension of E-waybills, exceptions may be granted. It can be:
|
|
|
|
|
- Government Notification: Businesses might not need to comply with the usual E-waybill extension criteria if a state makes formal notices permitting exemptions or offering alternative procedures in specific circumstances.
- Short Distance Transportation: Moving products within a certain radius and receiving special consideration, some states may offer exemptions for short-distance transportation.
- Emergency Situations: In emergency cases, exemptions could be taken into consideration to guarantee the uninterrupted flow of goods in emergency conditions.
- Pre-approved Periods for Specific Goods: Certain states may give exemptions under certain conditions during pre-approved extension periods for specific groups of commodities.
- Approved Trans-shipment Scenarios: States may grant exceptions for the extension of an E-waybill in situations when the movement of goods from one vehicle to another is authorized transshipment.
Also Read: Valid Reasons for E-waybill Extension: Understanding the Scenarios
Best practices for harmonizing E-waybill extension across states
Adopting standardized and effective procedures is necessary to harmonize E-waybill extensions across states. Initially, companies should make sure they are aware of any changes to the state-specific E-waybill requirements by keeping up with them.
Creating a centralized E-waybill management system can expedite and encourage consistency in the extension procedure. Maintaining open lines of communication with relevant authorities and ensuring that staff members are knowledgeable about state-specific rules are essential.
It is essential to invest in technological solutions that can adjust to various state rules to enable seamless and legal E-waybill extensions. Frequent training sessions can improve staff comprehension, and strict record-keeping procedures guarantee transparency.
Cooperation between companies and regulatory agencies can help standardize, which will promote a state-by-state unified strategy for E-waybill extensions.
Audit and verification of compliance with state-specific extension rules
Audit and verification of adherence to state-specific E-waybill extension requirements need comprehensive inspections and evaluations. Key elements for the audit and verification procedure are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Role of technology in managing diverse state extension requirements
Technology is essential to effectively handling the various state extensions for E-waybills. Centralized digital systems offer a uniform interface for compliance across several states, streamlining the extension process. Automatic methods can adjust to the regulations of each state, guaranteeing precise and prompt extensions.
With technology, firms can receive real-time notifications on regulatory changes. Automated technologies and E-waybill databases are integrated to improve accuracy and decrease human error. By using automated alerts and notifications, companies can take proactive measures to meet compliance requirements.
In essence, technology improves agility, transparency, and compliance with various state rules in addition to streamlining the E-waybill extension process.
Conclusion
In summary, managing the landscape of E-waybill extensions between states necessitates an intricate understanding of several laws. Through identification and adjustment to state-specific regulations, companies may guarantee smooth compliance and effective goods transportation.
Embracing technology, preserving open lines of communication, and keeping up with changing state-specific regulations are all necessary for harmonizing E-waybill extensions.
Businesses are working to increase the validity of E-waybills, which makes interstate logistics operations easier, more transparent, and consistent with the law.
Businesses can successfully negotiate the intricacies and cultivate a strong supply chain network that complies with the various regulations of each state by taking a proactive approach and maintaining constant awareness.
FAQs
Q1: Can I extend the validity of an E-waybill in any state?
No, the procedure and requirements for extending the validity of an E-waybill differ by state. Respecting the unique laws that apply to each state that has transportation rules is crucial.
Q2: What are common reasons for E-waybill extensions?
Depending on state laws, legitimate explanations might include unanticipated events, transshipment, or extraordinary circumstances.
Q3: Is the extension process the same for all states?
No, the laws governing E-waybill extensions vary from state to state. Understanding and adhering to each state’s particular rules is essential.
Q4: How can technology assist in managing state-specific extensions?
Technology provides a centralized platform, automating the extension process and adapting to diverse state regulations, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
Q5: Are there penalties for non-compliance with E-waybill extension rules?
Yes, non-compliance may lead to penalties. It’s crucial to adhere to state regulations to avoid disruptions and penalties.
Q6: Can I extend an E-waybill after it has expired?
Extending an E-waybill after expiration depends on state regulations. Some states may have provisions for extension after expiry under specific conditions.
Q7: How often should I check state-specific E-waybill extension requirements?
Regularly check for updates and changes in E-waybill regulations in each state to ensure ongoing compliance.
Q8: What documentation is required for E-waybill extensions?
Documentation may include the original E-waybill, extension request, approvals, and reasons for extension, as per state regulations.
Q9: Is there a specific timeline for notifying authorities about E-waybill extensions?
Yes, some states may have specific timelines for notifying authorities. Timely communication is essential to avoid non-compliance.
Q10: Can E-waybill extensions be exempted in certain circumstances?
Exemptions may be considered for force majeure events, government notifications, or specific state-approved scenarios, depending on the circumstances and state regulations.

