INTRODUCTION
An E-waybill serves as the digital document needed for the movement of any consignment and has a specific validity. But sometimes, we need to extend the validity of the E-waybill if the consignment has not reached the destination within the due time.
Moreover, in this blog post, we will explore the intricacies of an E-waybill extension, which plays a crucial role in logistics management.
Also Here, we will discuss the possible reasons behind extending the validity of an E-waybill and know the step-by-step procedure to ensure a seamless continuation of your good’s journey.
E-waybill Extension Criteria
If the validity of an E-waybill expires due to any unforeseen situation before the consignment reaches the final end, the validity can be extended in the following cases:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
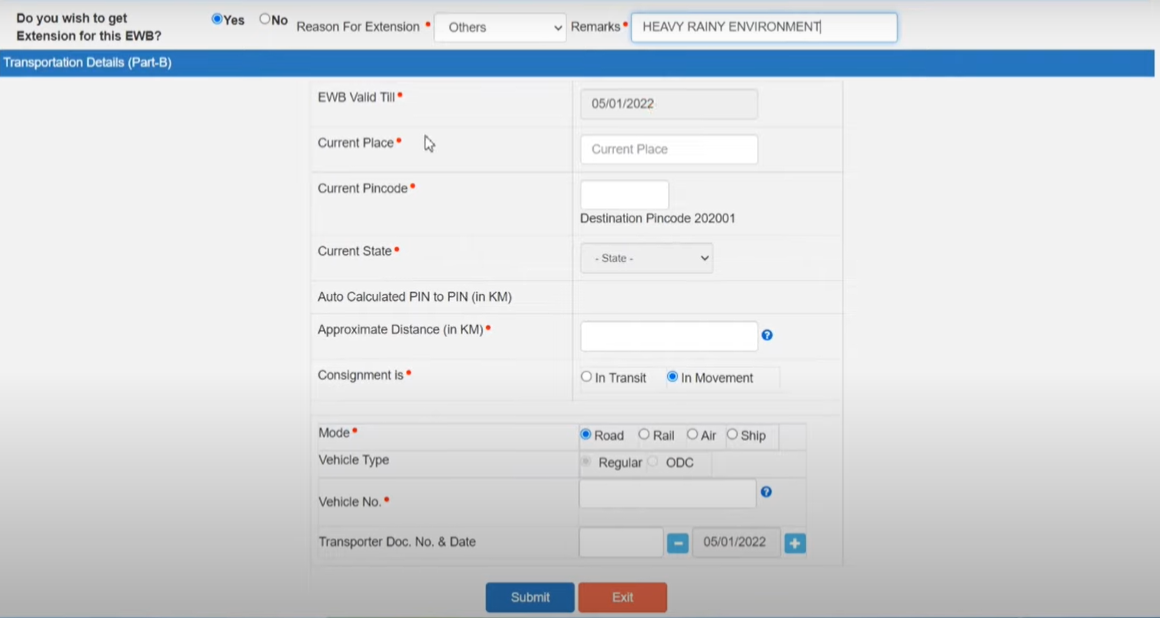
Legal Provisions for Extending E-waybill Validity
The legal provisions for extending an E-waybill are governed by the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime. Under Rule 138 of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Rules, 2017, an E-waybill can be extended by the person in charge of the conveyance for a further distance than what was originally mentioned, and the due reasons may be natural calamities, law and order issues, or any other exceptional circumstances.
It is important to note that as per the latest notifications and amendments, E-waybill should stay compliant with the current regulations, as updates may have occurred.
The authorities introduced the e-waybill in order to streamline the entire transportation process.
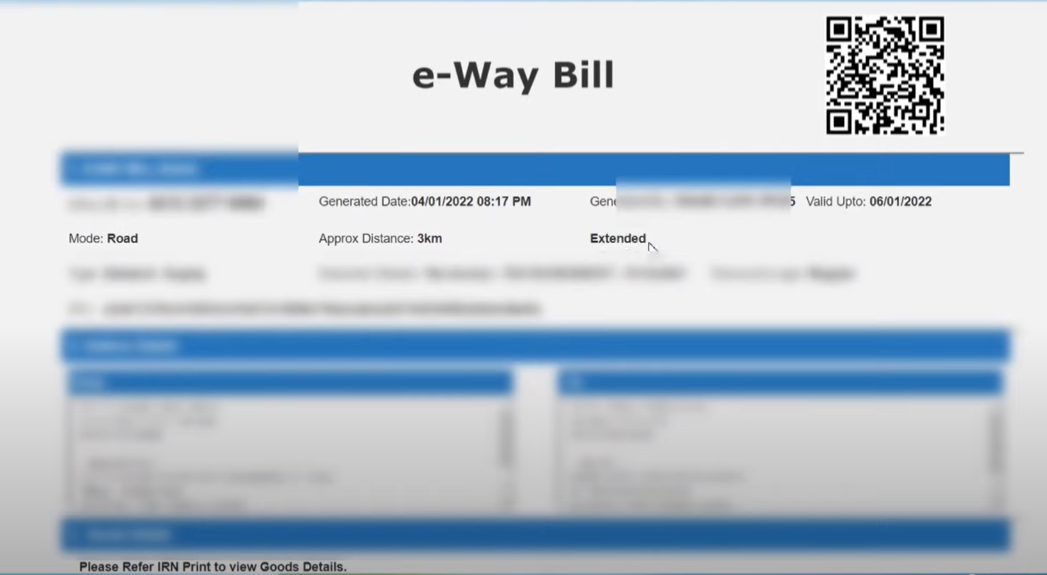
Also Read: How Long Does An E-Way Bill Remain Valid And What Needs To Extend Its Validity
Compliance Obligations for E-waybill Extension
Compliance obligations for E-waybill extensions typically involve adherence to regulations governing electronic documentation for the movement of goods. This includes accurate and complete information about the extended E-waybill, such as details about the consignment, transporter, and relevant tax invoices.
Additionally, businesses must stay updated on any changes in legislation related to E-waybills to maintain compliance with the evolving regulatory landscape. Also, Regular audits and reviews of E-waybill processes are essential to identify and rectify any non-compliance issues promptly.
Documentation Requirements for Extending E-waybill Validity
To extend the E-waybill, you must submit some valid documents and information to comply with the extension requirements. Also, some of them are below:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reporting Obligations for Extended E-waybill Validity
The specifics of reporting obligations for extended E-waybill validity might differ based on the country or region’s regulations. Moreover, in India, the E-waybill system mandates the generation of these bills for the movement of goods exceeding a certain value or distance.
If there are changes or extensions to the validity period, it’s crucial to adhere to the reporting requirements set by the tax or transportation authorities. Also, these might involve updating the system with the extended validity details, reasons for extension, and any necessary supporting documentation.
Always consult the official guidelines or reach out to the relevant authorities, such as the tax department or transportation regulatory bodies, for precise information on reporting obligations related to extended E-waybill validity in your specific area or country.
Challenges in Extending E-waybill Validity
Below given are some of the challenges you may face while extending the E-waybill validity:
| Dynamic Business Scenarios |
|
| Data Integrity and Security |
|
| Technological Challenges |
|
Exemption Considerations for Specific Scenarios
Moreover, specific transports exempted from E-way bill rules are:
- Liquefied petroleum gas for supply to household and non-domestic exempted category customers.
- Kerosene oil sold under the Public Distribution System (PDS)
- Postal baggage transported by the Department of Posts
- Natural or cultured pearls and precious or semi-precious stones; precious metals and metals clad with precious metal.
- Jewelry, goldsmiths’ and silversmiths’ wares, and other articles.
- Currency
- Used personal and household effects
- Unworked and worked coral
- Goods transported are alcoholic liquor for human consumption, petroleum crude, high-speed diesel, petrol, natural gas, or aviation turbine fuel.
- Goods being transported are not treated as supply under Schedule III of the Act. Schedule III consists of activities that would neither be a supply of goods nor service like service of an employee to an employer in his employment, functions performed by MP, MLA, etc.
- Goods transported are empty cargo containers.
- Goods other than de-oiled cake being transported are specified in notification No. 2/2017– Central Tax (Rate) dated the 28th of June 2017. A few of the goods that are include in the above notification are as follows:
- Curd, lassi, buttermilk
- Fresh milk and pasteurized milk do not contain added sugar or other sweetening matter
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Unprocessed tea leaves and unroasted coffee beans
- Live animals, plants, and trees
- Meat
- Cereals
- Unbranded rice and wheat flour
- Salt
- Items of educational importance (books, maps, periodicals)
- Goods exempted under notification No. 7/2017– Central Tax (Rate) dated 28th June 2017 (supply by CSD to unit-run canteens and authorized customers) and notification No. 26/2017– Central Tax (Rate) dated 21st September 2017 (consists of heavy water and nuclear fuels).
Best Practices for Timely E-waybill Extension
Also, Here are the best practices to extend the E-waybills in a timely manner:
- Know the Validity Period: An E-waybill is valid for a certain number of days depending on the distance to be traveled. So, ensure you are aware of the validity period and the time of its expiry.
- Plan Well Before: Initiate the process for E-waybill extension in advance well before the expiry date comes. Last-minute extensions might lead to delays or some penalties.
- Gather Necessary Information: At the time of extension, you may need to submit all relevant information required for extension, such as the original E-waybill number, transportation details, consignment details, and reasons for extension. So, keep all these handy.
- Always Use Authorized Portals: For extension, login to authorized government portals or apps designated for E-waybill generation and extension. Also, This will safeguard you from any data theft.
- Document Verification: Try to submit all the supporting documents related to the extension request are accurate and up-to-date. Also, this includes invoices, transport details, and any other necessary paperwork.
- Timely Submission: Submit the extension request well before the expiry of the current E-waybill. Also, this allows ample time for processing and avoids any disruptions in the transportation process.
- Keep A Follow-up: Check the status of the extension request on a regular basis.
Also Read: How Can I Extend The E-Way Bill Validity With Ease?
Audit and Verification of Extended E-waybills
Also, Here are some audit and verification steps that authorities perform for E-waybill extension:
-
Audit and verification of E-waybills in government shipments are crucial in making the process transparent and compliant. Additionally, E-waybills are electronic documents that contain details of the goods, along with the information of the consignor and consignee.
- During the audit process, government authorities review E-waybills to confirm the accuracy of information. Also, this involves cross-referencing details of the consignor, consignee, goods description, the time period, and the valid reason for delay.
- Verification procedures may involve real-time tracking of shipments using GPS technology or other tracking systems to ensure the current location of goods and the valid reason for delay. Additionally, authorities may compare E-waybill data with other relevant documents, such as invoices and tax records, to verify the consistency of information across different channels.
- Ensuring the integrity of the E-waybill system is vital for preventing tax evasion, fraud, and unauthorized movement of goods. Regular audits and verifications contribute to a robust system that enhances the overall efficiency and trustworthiness of government shipments.
Role of Technology in E-waybill Extension
The authorities introduced the e-waybill to smoothen the entire transportation process. And with the implementation of it, the entire process has become digital, making the process of extension and compliance easier than before. Therefore, The role of technology in E-waybill extension is immense and has brought about significant changes.
| Automation of E-waybill Extension | The process of E-waybill extension has become automated with the use of technology. The GST portal has reduced the hazards of manual entry and a significant amount of errors. It automatically calculates tax, time, and duration. |
| Real-Time Tracking and Extension | Technology enables the business to track their shipments as well as extend the validity of the E-waybill if it expires. The real-time tracking has made the entire process easy, transparent, and efficient. |
| Data Analysis | The role of technology can not be overshadowed here. It gives the business power of data analytics in E-waybill filling. And with the technology evolution, we can expect more advancements in E-waybill extension. |
Also Read: Benefits of E-way Bill Registration
Conclusion
So, Extension of the validity period of an E-waybill is a straightforward process that gives flexibility to businesses in transporting their goods. Moreover, a timely extension can reduce the disruption in logistics and make the supply chain smooth and compliant. With the above-mentioned guidelines on when and how to extend the E-waybill, one can make his entire system more easy and hassle-free.
FAQs
Q1. What are the possible reasons for an E-way bill extension?
One can extend the validity of the E-way bill, if the consignment is not reaching the destination within the validity period due to exceptional circumstances like natural calamity, law and order issues, trans-shipment delay, accident of conveyance, etc.
Q2. What happens if the E-way bill expires?
If the validity of the e-way bill expires, you cannot legally move the goods. However, under circumstances of ‘exceptional nature and trans-shipment’, the transporter may extend the validity period after updating the valid reason for the extension and the details.
Q3. What is the penalty for not raising the E-way bill?
For moving goods without the cover of an invoice and E-way bill constitutes an offense and attracts a penalty of Rs. 10,000 or the tax sought to be evaded (whichever is greater).
Q4. What are the roles and responsibilities of the E-way bills?
The e-way bill is an essential document for transporting all goods except those exempted under the notifications or rules. Movement of handicraft goods or goods for job-work purposes under specified circumstances also requires an E-way bill even if the value of the consignment is less than fifty thousand rupees.
Q5. What is the E-way bill time extension?
You cannot extend the validity of the E-waybill anytime you want. It can only be extended 8 hours before or 8 hours after the expiry date.
Q6. When will the e-way bill become mandatory?
If the value of goods being transported is less than Rs. 50,000, the creation of an E-way bill is optional, and it is also mandatory if the supplier is not GST-registered but the receiver is GST-registered. Also, The GST-registered person is required to ensure compliance in such cases.
Q7. What are Part A and B in the E-way bill?
The E-Way Bill, or GST EWB, is divided into two parts:- Part A and Part B. Part A contains the products’ information, while Part B contains the vehicle’s identification number.
Q8. How do I extend my multi-vehicle e-way bill?
First, generate the e-way bill with the source and destination as per the document/invoice. Also, Carry out the first leg of movement of the consignment up to the transhipment. Choose the ‘Change to Multi-vehicle’ option and update the e-way bill for multi-vehicle movement.
Q9. What happens if the e-way bill expires?
Generally, the GST Authorities, in such cases where the valid period of the e-way bill has expired, take action under section 129 of the CGST Act. They pass the order of detention and penalize accordingly.
Q10. From where to find the information on would-be-expiring E-waybills?
You can find the information on your would-be-expiring E-way bills for 4 days starting from the current date. Also, if you want to view the list, you should log into the official website of E-way Bill and navigate through different menus based on the instructions.

