I. Introduction
In the GST regime, a Casual Taxable Person (CTP) holds a distinct status designed for those who periodically conduct business transactions without a fixed place of business in the taxable territory. Understanding the role and regulations surrounding CTPs is essential for individuals and businesses participating in temporary or seasonal commercial activities.
This blog sets the stage for an in-depth exploration of what it means to be a CTP, the process involved in registering, the benefits of such registration, and the associated obligations under the GST framework. By the end of this guide, you will be well-informed about how a Casual Taxable Person status could impact business operations and compliance requirements under GST.
II. Applicability of Casual Taxable Person Status
Under GST law, a Casual Taxable Person is defined as someone who undertakes transactions involving the supply of goods or services on an occasional basis in a jurisdiction where they have no fixed place of business. This Casual Taxable Person Definition is key to understanding the broader implications and responsibilities under GST.
To qualify as a CTP, an individual or business must engage in activities that are project-based, or for a limited period, within a state where they are not normally established. The status is specifically applicable during events like exhibitions, seasonal businesses, or short-term projects where the person wishes to supply goods or services.
III. Registration Process for Casual Taxable Persons
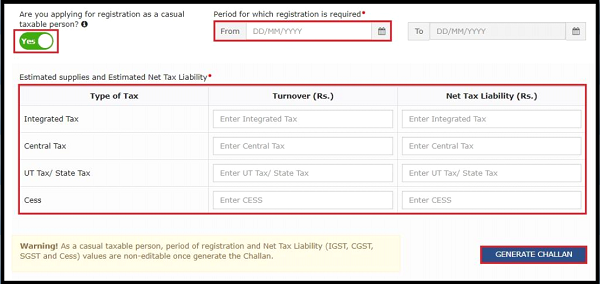
Registering as a Casual Taxable Person under GST is a necessary process for individuals or businesses planning to undertake temporary taxable activities in a state where they do not have a fixed business establishment. Here’s a detailed guide on how to register as a Casual Taxable Person, ensuring that you comply with all relevant GST regulations:
- Online Application: Access the official GST portal to complete Form GST REG-01, part B. Enter basic business information and details of the planned activities.
- Documents Required: Upload necessary documents including identity and address proof, details about your business activities, bank account information, and a declaration of expected turnover.
- Advance Tax Payment: Estimate and pay your GST liability in advance for the duration of the registration. This payment will be credited to your temporary GST account.
- Validity and Extension: CTP registration is valid for up to 90 days. For longer activities, submit Form GST REG-11 for an extension before the current registration expires.
- Completion of Registration: Post payment and document verification, receive your CTP registration certificate with a unique GSTIN within three working days.
- Final Return: File Form GSTR-10 as a final return after your business activities end, to conclude your GST obligations.
By following these steps on how to register as a Casual Taxable Person, individuals and businesses can ensure that they meet all the GST compliance for Casual Taxable Persons requirements and leverage the benefits of their temporary registration without facing any legal hurdles. This process underscores the importance of understanding and adhering to GST regulations, particularly for those engaging in short-term commercial activities across state lines.
IV. Benefits of Being a Casual Taxable Person
Obtaining the status of a Casual Taxable Person under the GST framework offers several unique advantages, particularly for those engaged in short-term, project-based, or seasonal business activities across different states.
- Operational Flexibility: The primary benefit of registering as a CTP is the operational flexibility it offers. Businesses can participate in trade fairs, exhibitions, or undertake short-term projects in different states without the need for a permanent GST registration in those states. This flexibility allows businesses to explore new markets and opportunities without committing to long-term obligations.
- Tax Benefits: As CTPs, businesses are eligible to claim input tax credits on goods and services used exclusively for the activity that qualifies them as CTPs. This can significantly reduce the cost of operations in a state where they do not have a fixed base. Additionally, CTPs can enjoy simplified tax compliance procedures during their active registration period, which can include benefits like fewer compliance filings compared to regular taxpayers.
Incorporating these Benefits of Casual Taxable Person Registration into strategic planning allows businesses to maximise their operational effectiveness and manage costs efficiently while ensuring compliance with GST laws.
V. Obligations and Responsibilities
While the status of a Casual Taxable Person offers several benefits, it also comes with specific obligations and responsibilities to ensure compliance with GST regulations.
- Compliance Requirements: CTPs must adhere to a stringent set of GST compliance requirements. This includes the necessity to register in advance of undertaking any taxable activity, the obligation to pay estimated GST upfront based on anticipated turnover, and the need to file periodic GST returns during the registration period. These requirements ensure that the CTP remains compliant with the tax laws of the state where they are temporarily conducting business.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining detailed and accurate records is crucial for CTPs. This includes records of sales and purchases, a detailed account of inventory used for business purposes, and documentation of all tax payments made during the registration period. Proper record keeping not only facilitates easier compliance and reporting but also aids in the accurate calculation and claiming of input tax credits.
Understanding and managing these responsibilities is essential for GST Compliance for Casual Taxable Persons. Adhering to these guidelines not only helps in avoiding penalties but also ensures smooth operation within the regulatory framework, making the Benefits of Casual Taxable Person Registration more tangible and effective for businesses engaged in temporary or seasonal ventures.
VI. Limitations and Challenges
While the status of a Casual Taxable Person offers flexibility and specific tax benefits, there are inherent limitations and challenges that come with this classification under the GST framework.
- Duration Limit: One of the primary limitations for CTPs is the temporary nature of the registration. It is typically granted for a period up to 90 days and can be extended for another 90 days if necessary. This finite duration may limit the scope of projects CTPs can undertake, potentially impacting long-term contracts and ongoing business engagements that extend beyond the allowed registration period.
- Operational Constraints: CTPs face several operational challenges due to the lack of a permanent business establishment. This can result in difficulties in establishing a stable customer base, logistical challenges in managing supplies and inventories, and complications in setting up temporary operations in new locations. These factors can affect the operational efficiency and scalability of their business ventures.
- Market Perception: Being a CTP might influence how other businesses and consumers perceive the company. Some may view CTPs as less stable or reliable compared to businesses with permanent GST registration, potentially affecting business relationships and market opportunities.
These challenges necessitate careful consideration by businesses when deciding to operate as CTPs and highlight the importance of strategic planning and management of GST Compliance for Casual Taxable Persons.
VII. Comparison with Regular Taxpayers
| Aspect | Casual Taxable Person (CTP) | Regular Taxpayer |
| Registration Requirement | Required for specific events/projects in a state without a permanent base. | Required for continuous business operations with a fixed establishment. |
| Tax Payments | Advance tax payment based on estimated turnover for the registration period. | Tax payments based on actual business transactions, filed monthly or quarterly. |
| Return Filing | Returns are to be filed for the period of registration only, usually monthly. | Regular filing of returns, typically monthly, quarterly, or annually depending on the turnover. |
| Duration of Registration | Temporary; valid for the period specified, usually up to 90 days, extendable. | Permanent as long as the business is operational unless cancelled. |
| Input Tax Credit | Can claim input tax credit only for the goods/services used during the active registration period. | Can continuously claim input tax credits on business-related purchases. |
| Compliance Burden | Higher due to the need to estimate taxes and comply within a short timeframe. | Steady compliance with regular intervals for filing and audits, which can be planned. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to operate in multiple states without permanent registration in each. | Requires registration and compliance in every state where there is a fixed place of business. |
| Audit and Scrutiny | Likely less scrutiny due to the temporary nature and shorter operation span. | Regular audits based on turnover and other criteria, with more frequent scrutiny. |
VIII. Case Studies and Examples
Case Study 1: Seasonal Handicrafts Seller
A handicraft seller from Rajasthan frequently participates in seasonal markets across different states, especially during festival seasons. By registering as a CTP, the seller was able to legally sell products in other states without establishing a permanent base, significantly increasing sales volumes during peak seasons. The key lesson from this case is the importance of timely CTP registration before seasonal spikes, ensuring compliance while capitalising on high market demand.
Case Study 2: Event Management Company
An event management company based in Delhi often organises large-scale corporate events in various states. By adopting the CTP status, the company managed to streamline its operations across state lines without the hassle of long-term GST compliance in each state. This case underscores the benefit of CTP status for businesses requiring operational flexibility across different jurisdictions, enabling them to focus on delivering high-quality services without administrative burdens.
Case Study 3: IT Contractor
An IT contractor undertook a three-month project in a state where they had no permanent office. Registering as a CTP allowed them to manage the project effectively, comply with local GST laws, and optimise their tax liabilities through input tax credits. The contractor learned the importance of accurate and upfront tax estimations to avoid financial discrepancies at the project’s conclusion.
Impact Assessment
These examples collectively demonstrate that adopting the CTP status can lead to enhanced market reach and operational flexibility. For businesses engaging in temporary or project-based activities, being a CTP reduces the administrative overhead associated with permanent GST registrations and compliance in multiple states. However, the businesses must meticulously plan their tax responsibilities and ensure they fully understand local GST regulations to avoid potential pitfalls.
IX. Conclusion
In conclusion, the Casual Taxable Person status under GST offers pivotal benefits for businesses undertaking temporary projects across different states, allowing them to navigate tax compliance with agility. Businesses must carefully consider their project durations and operational scopes to determine if this registration aligns with their strategies. Adapting to this status can significantly streamline tax processes for transient commercial activities, ensuring compliance while maximising operational efficiency.
Also Listen: How to create E-way Bill With CaptainBiz
X. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is a Casual Taxable Person under GST?
A Casual Taxable Person (CTP) under GST is someone who occasionally undertakes transactions involving the supply of goods or services in a territory where GST is applicable but does not have a fixed place of business. This definition is crucial for understanding Casual Taxable Person GST regulations and compliance requirements.
-
What are the benefits of registering as a Casual Taxable Person?
Registering as a CTP allows individuals or businesses to legally undertake short-term business activities without a permanent base in the location. Benefits of Casual Taxable Person Registration include legal compliance, eligibility to claim input tax credit, and the ability to participate in seasonal or temporary markets without extensive regulatory burdens.
-
How can someone register as a Casual Taxable Person?
To register as a Casual Taxable Person, one must apply through the GST portal before undertaking business activities. The process involves submitting a declaration form and providing a bank guarantee or a deposit equal to the expected GST liability for the period of registration, which is usually valid for three months and can be extended.
-
Who needs to understand the Casual Taxable Person definition?
Businesses and individuals planning to temporarily supply goods or services in different states or territories without a fixed place of operation should understand the Casual Taxable Person Definition to ensure they comply with GST laws and avoid penalties.
-
What does GST compliance entail for a Casual Taxable Person?
GST Compliance for Casual Taxable Persons includes obtaining a temporary registration, filing tax returns for the active period, paying estimated taxes in advance, and keeping accurate records of all transactions. Compliance ensures transparency with tax authorities and helps avoid financial discrepancies.
-
Are there specific documentation requirements for a Casual Taxable Person GST registration?
Yes, documentation for a Casual Taxable Person GST registration typically includes identity proof, address proof, and details of the business activity planned. Additionally, advance payment of GST estimated for the duration of registration is required.
-
How long does the Casual Taxable Person registration last?
A Casual Taxable Person’s registration is valid for a period not exceeding three months. However, it can be extended if the business activity continues beyond the initial estimated duration, subject to GST authority approval.
-
What happens if a Casual Taxable Person fails to comply with GST regulations?
Non-compliance with GST regulations can lead to penalties, denial of tax credits, and revocation of registration. Staying informed about GST Compliance for Casual Taxable Persons is crucial to avoid such issues.
-
Can a Casual Taxable Person claim input tax credits?
Yes, one of the significant Benefits of Casual Taxable Person Registration is the ability to claim input tax credits for goods and services used solely for business purposes, which can significantly reduce the overall GST liability.
-
What are the primary challenges faced by a Casual Taxable Person under GST?
Challenges include managing advance tax payments, ensuring accurate and timely filings during the active business period, and understanding the complexities of GST regulations without a permanent base in the location. These challenges underscore the importance of careful planning and compliance management for casual traders.