Yes, businesses can indeed claim input tax credits on taxes paid for inputs and services used in the production of goods or services.Yes, businesses can indeed claim input tax credits on taxes paid for inputs and services used in the production of goods or services.
The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax in India, consequently, has replaced a series of tax policies. However, this replacement has not been simple. This new taxation policy had to cover all the grounds of the previous taxes while ensuring a more just and sustainable economic balance.
Therefore, GST involves numerous slabs that are devised specifically for a range of goods and services. This is also why having a deeper understanding of the dynamics of GST tax slabs is essential for businesses and consumers. However, if you do not know much about it, read the article below.
What are GST Tax Rates?
Goods and Services Tax, therefore, is a cumulative indirect tax system in India that replaced various taxes like excise duty, VAT, and service tax. Moreover, it simplifies the tax structure by introducing a single tax on goods and services. Essential items like food, grains, and healthcare services are usually taxed at lower rates, whereas luxury items attract higher rates.
To calculate GST, one must multiply the taxable amount by the applicable GST rate and then divide by 100 to obtain the GST amount. For instance, if an item costs ₹100 and the GST rate is 18%, the GST amount would be ₹18. The total price, including GST, is then ₹118. This method ensures transparency and streamlines the taxation process, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
Why are GST Tax Slabs Important?
GST tax slabs are crucial as they determine the rates at which services and goods are taxed, impacting both businesses and consumers. Some other reasons why GST tax slabs are essential are:
1. Simplification
GST tax slabs, consequently, bring uniformity by categorizing goods and services into predefined tax rates. Additionally, this simplifies the tax structure and significantly reduces confusion.
2. Progressive Taxation
Different tax slabs, therefore, allow for a progressive taxation system, where goods are taxed according to their essentiality. This provides relief to the common person while posing the same level of burden for the rich.
3. Revenue Generation
The variation in tax rates, consequently, helps generate revenue for the government. Moreover, this ensures a balanced approach to taxation across different sectors and income groups.
4. Incentivising Essential Services
Furthermore, lower tax slabs on essential services like healthcare and education effectively incentivize the growth of these sectors. This further makes crucial services more accessible to the public.
5. Addressing Economic Disparities
Moreover, GST slabs can be used strategically to address economic disparities. Additionally, they can provide relief to economically weaker sections through lower tax rates on essential commodities.
6. Consumer Behavior and Demand
Furthermore, the different tax slabs significantly influence consumer behavior and demand patterns. As a result, individuals may opt for goods and services in lower tax brackets. This further helps stimulate certain sectors of the economy.
GST Rate Structure in India
Moreover, India’s Goods and Services Tax rate structure encompasses various slabs to cover a range of goods and services, thereby ensuring a comprehensive and subtle taxation system. Specifically, the primary GST slabs for regular taxpayers include 0% (nil-rated), 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.

Source – https://www.livemint.com/Politics/OuTNv0usNfIiRBklKa5B1O/GST-rates-to-be-between-5-and-28.html
GST Rates for Regular Taxpayers
| GST Rate | Categories of Goods/Services |
| 0% | Nil-rated items, essential goods like certain food items |
| 5% | Essential goods, some services, and items of mass consumption |
| 12% | Processed food, computers, and other necessary services |
| 18% | Mobile phones, electronics, and most goods and services |
| 28% | Luxury items such as cars, aerated drinks, and high-end services |
Moreover, taxable composition persons pay GST at lower rates like 5%, 1.5%, or 6% on their turnover. Tax Deducted at Source and ax Collected at Source under GST have rates of 2% and 1%, respectively.
Apart from this, the Integrated GST (IGST) is applicable for interstate supplies. On the other hand, intrastate supplies involve the sum of Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST).
Cess Rates
In addition to standard GST tax rates for goods and services, the law imposes cess on specific items like cigarettes, tobacco, aerated water, gasoline, and motor vehicles. Cess rates, ranging from 1% to 204%, therefore provide an additional mechanism to regulate and tax certain goods.
Classification of Items Under the GST in India
In India, to promote affordability and ease for specific sectors, certain goods and services are, therefore, exempted from the Goods and Services Tax. Specifically, here’s a list of items exempt from GST:
| GST Tax Slabs | Goods | Services |
| 5% |
|
|
| 12% |
|
|
| 18% |
|
|
| 28% |
|
|
This detailed classification, therefore, helps in understanding the diverse range of goods and services taxed under different GST slabs in India.
What are the Goods and Services Exempted From GST in India?
This detailed classification, therefore, significantly helps in understanding the diverse range of goods and services that are systematically taxed under different GST slabs in India. Specifically, the goods exempted from GST in India include:
| Types of goods | Examples |
| Live animals | Asses, sheep, cows, poultry, goats, etc. |
| Meat | Fresh and frozen meat of sheep, horses, goats, cows, pigs, etc. |
| Fish | Fresh or frozen fish |
| Natural products | Honey, pasteurized and fresh milk, eggs, cheese, etc. |
| Live trees and plants | Bulbs, foliage, flowers, roots, etc. |
| Vegetables: | Tomatoes, onions, potatoes, etc. |
| Fruits | Bananas, apples, grapes, etc. |
| Dry fruits | Walnuts, cashew nuts, etc. |
| Tea, coffee, and spices | Coffee beans, turmeric, tea leaves, ginger, etc. |
| Grains | Wheat, oats, rice, barley, etc. |
| Products of the milling industry | Various kinds of flours |
| Seeds | Flower seeds, cereal husks, oil seeds, etc. |
| Water | Tender coconut water, mineral water, etc. |
| Baked goods | Bread, puffed rice, pizza base, etc. |
| Fossil fuels | Electrical energy |
| Drugs and Pharmaceuticals | Contraceptives, human blood, etc. |
| Fertilizers | Goods and organic manure |
| Beauty products | Bindi, kumkum, kajal, etc. |
| Waste | Municipal waste, sewage sludge, etc. |
| Ornaments | Glass and plastic bangles, etc. |
| Newsprint | Judicial stamp paper, rupee notes, envelopes, etc. |
| Printed items | Printed books, newspapers, maps, etc. |
| Fabrics | Raw silk, khadi, silkworm cocoon, etc. |
| Hand tools | Hammer, spade, etc. |
| Pottery | Clay lamps, earthen pots, etc. |
Moreover, the services that are exempted from GST in India are
| Types of services | Examples |
| Agricultural services | Cultivation, harvesting, supplying farm labour, warehouse-related activities, renting agricultural machinery, services provided by a commission agent or Board for buying or the Agricultural Produce Marketing Committee or selling agriculture produce, etc. |
| Government services | Postal service, services by a foreign diplomat in India, transportation of people or goods, services offered to diplomats, services offered by the Reserve Bank of India, etc. |
| Transportation services | Transportation of goods by road, water, rail, etc., payment of toll, transportation of goods where the cost of transport is less than INR 1500, transportation of passengers by air, etc. |
| Judicial services | Services offered by the partnership firm of advocates, arbitral tribunal, or senior advocates to an individual or business entity whose aggregate turnover is up to INR 40 lakhs |
| Educational services | Transportation of faculty or students, examination services, mid-day meal scheme, services offered by IIMs, etc. |
| Medical services | Services offered by ambulances, charities, medical professionals, veterinary doctors, etc., do not include hair transplants or cosmetic or plastic surgery. |
| Organizational services | Services offered by exhibition organizers for tour operators for foreign tourists, international business exhibitions, etc. |
| Other services | Services offered by GSTN to the Central or State Government or Union Territories, circuses, admission fees payable to theatres, sports events, etc., which charge a fee up to INR 250 |
This exemption list, therefore, ensures that crucial services and everyday essentials remain accessible to all sections of society.
Also Read: Understanding GST Threshold Limits And Exemptions: Essential Guide
What are the Latest GST Rates in India in 2023?
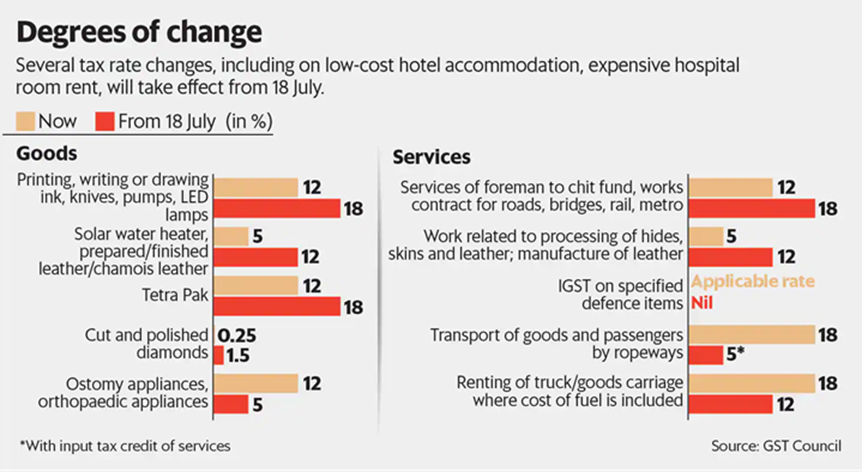
Source – https://www.livemint.com/economy/changes-in-gst-rates-to-be-applicable-from-18-july-11656525911095.html
The latest GST rate revision was made in the 50th GST Council Meeting on 11th July 2023. It was chaired by the Indian Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman. Consequently, this meeting witnessed revisions in GST rates for several items. Here are the updated rates:
| Items | Old GST Rate | New GST Rate |
| Food and Beverages in Cinema Halls | 18% | 5% |
| Uncooked, Unfried, and Extruded Snack Palettes | 18% | 5% |
| Cancer-Related Medicine | – | Exempt |
| Food for Special Medical Purposes (FSMP) | – | Exempt |
| Medicines for Rare Diseases | – | Exempt |
| Imitation Zari Thread or Yarn | 12% | 5% |
| Fish Soluble Paste | 18% | 5% |
| LD Slag | 18% | 5% |
| Casinos, Online and Horse Racing (Online Gaming) | 18% | 28% |
These revisions aim to provide relief and encourage accessibility, especially in the healthcare sector, while adjusting certain entertainment and gaming service rates.
Also Read: New GST Rates 2023 – List Of Latest Goods And Service Tax Rates Slabs
Why do GST Rates Keep on Increasing or Decreasing?
GST tax rates for services and goods may fluctuate due to various factors influencing a country’s economy. Some of the major influencing factors are:
1. Economic Conditions
GST rates, therefore, majorly depend on the country’s economic health. Therefore, in times of economic downturns, rates may decrease to encourage spending and boost economic activity. However, during strong economic phases, rates may increase to prevent overheating and manage inflation.
2. Revenue Requirements
GST rates may, therefore, be altered to align with budgetary requirements if there’s a shortfall or surplus. Consequently, this ensures adequate funds for public services and development initiatives. Thus, changes in government revenue needs also drive adjustments in GST rates.
3. Inflationary Pressures
In an inflating economy, GST tax rates for services and goods might, therefore, be strategically adjusted to counter rising prices effectively. As a result, this strategic move aims to stabilize the cost of goods and services, thereby preventing excessive inflationary pressures on consumers.
4. Policy Adjustments
Moreover, government policies play a crucial role in GST rate changes. For instance, lowering GST rates can encourage growth in targeted sectors. Thus, rates may be tweaked to support specific industries to align with broader objectives.
5. International Factors
Global economic conditions and trade dynamics also influence GST tax rates for goods and services linked to international markets. Also, such changes occur in response to shifts in global trade patterns and economic trends.
6. Sector-Specific Considerations
In an inflating economy, GST tax rates for services and goods might, therefore, be strategically adjusted to counter rising prices effectively and, as a result, help stabilize the overall cost of living. Therefore, certain sectors may experience rate adjustments to address industry concerns, stimulate growth, and ensure equitable taxation.
Indeed, these fluctuations are part of a dynamic system that aims to strike a balance between economic stability, revenue generation, and the welfare of citizens.
Conclusion
In conclusion, comprehending the intricacies of GST tax rates serves as a guiding compass through the complex tax structure in India. Additionally, with tiered GST tax slabs and meticulous classification of goods and services, the GST system is crafted to strike a delicate balance. Moreover, this equilibrium extends beyond mere revenue generation, encompassing the broader goals of stimulating economic growth and sustainability.
Also Read: GST: The Complete Guide
Also Listen: Calculate Your GST within Seconds
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is RCM in GST?
The reverse charge mechanism (RCM) in GST, therefore, involves the buyer paying the tax directly to the government, ensuring compliance and streamlining the tax collection process.In addition, this mechanism is often applicable to specific goods and services, ensuring a streamlined tax collection process.
Q2. Who is Eligible for RCM?
Businesses dealing with legal services or consultancy, as well as specified goods like silk yarn, cashews, etc., may, therefore, be eligible for RCM under GST.
Q3. What is the HSN and SAC Code?
HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) and SAC (Services Accounting Code) are codes used to classify goods and services for GST invoicing and taxation.
Q4. How Often do GST Rates Change in India?
GST rates in India, therefore, may change based on economic conditions and government policies. These changes usually occur during the budget sessions or as needed.
Q5. What is the Impact of GST on Small Businesses?
GST tax rates for small businesses may have compliance challenges initially, but it also streamlines their taxation. It, as a result, promotes a unified tax system, thereby easing inter-state trade.
Q6. How do Anti-Profiteering Measures Work Under GST?
Anti-profiteering, therefore, ensures businesses pass on GST benefits to consumers by reducing prices. Consequently, a National Anti-Profiteering Authority monitors its compliance.
Q7. Can Businesses Claim GST Input Tax Credit?
Yes, businesses can indeed claim input tax credits on taxes paid for inputs and services, thereby contributing to the cost-effectiveness of producing goods or services. Consequently, this helps reduce the overall tax burden, ensuring a more efficient and cost-effective production process.
Q8. What is the Rationale Behind Exempting Certain Items From GST?
Exempting essential goods and services from GST, therefore, ensures greater affordability and accessibility for consumers. It further supports basic needs and maintains the socio-economic balance.
Q9. How can Businesses Stay Updated on Changes in GST Rates?
Businesses can stay updated about GST rate changes by regularly checking official GST portals, attending seminars, and in addition, consulting tax professionals for real-time information. Moreover, staying informed allows businesses to make timely adjustments and comply with the latest regulations.
Q10. What are the Four Types of GST?
The four types of GST are CGST (Central GST), SGST (State GST), IGST (Integrated GST), and UTGST (Union Territory GST), each with different territorial boundaries.

